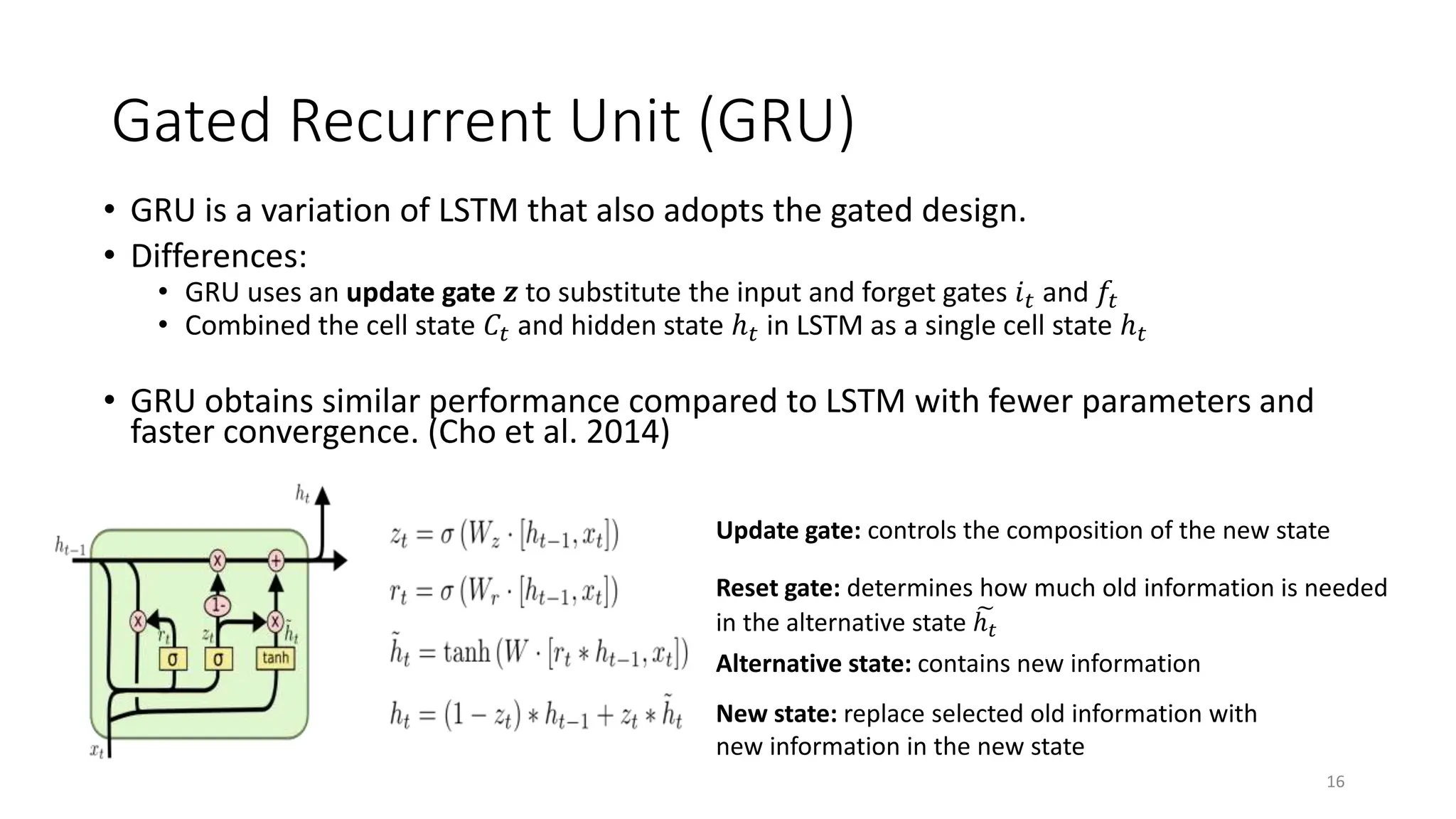
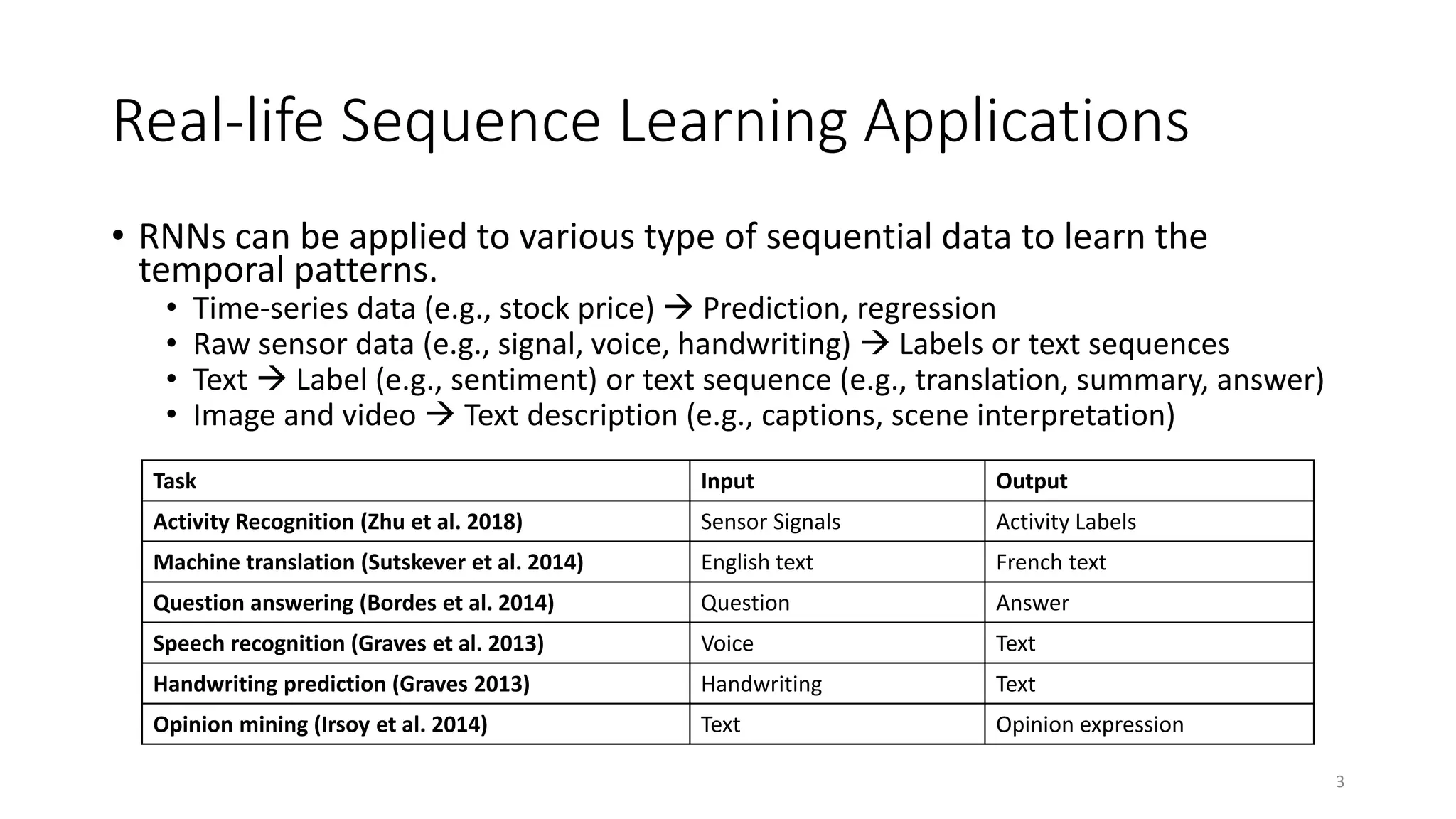
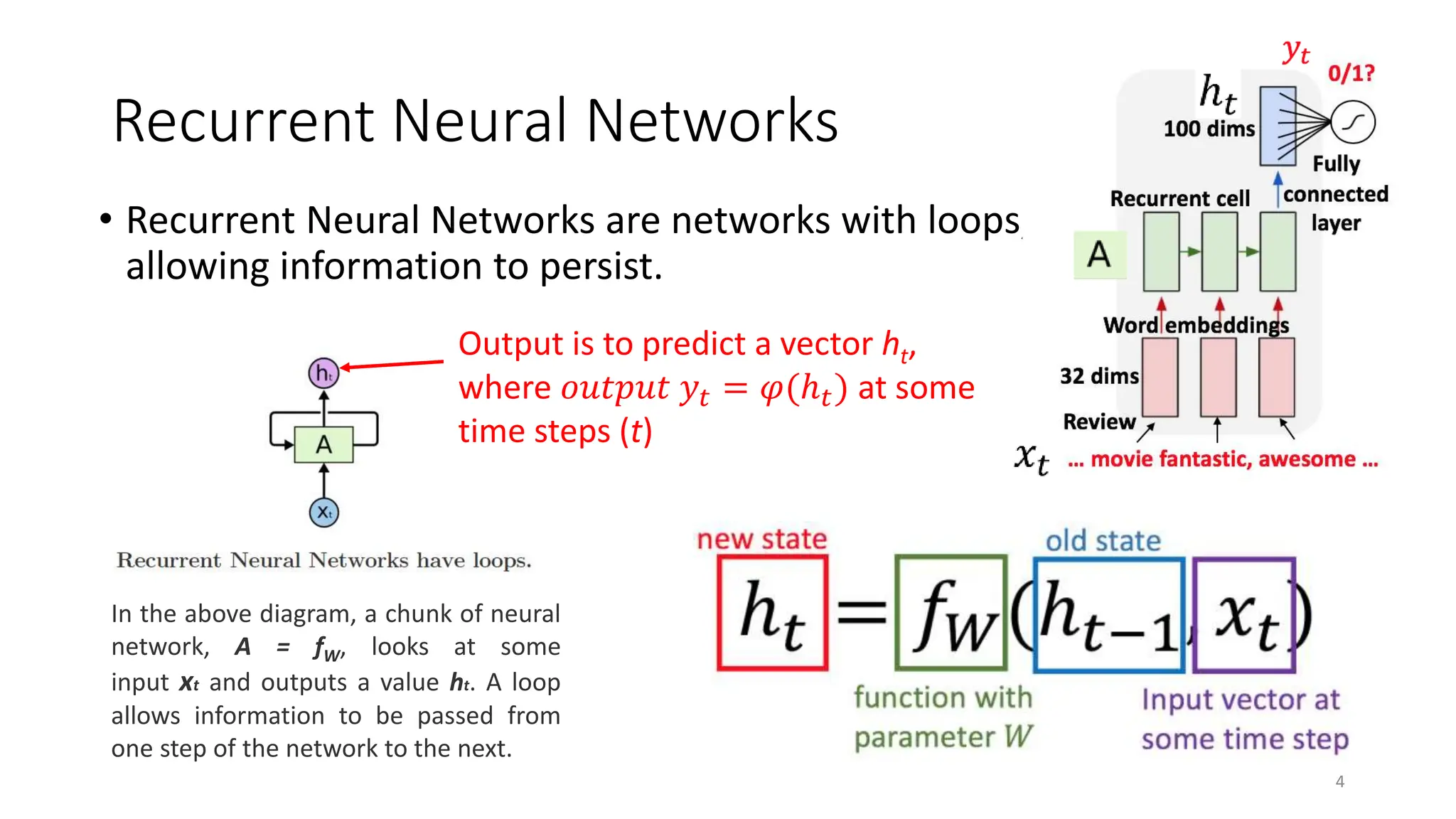
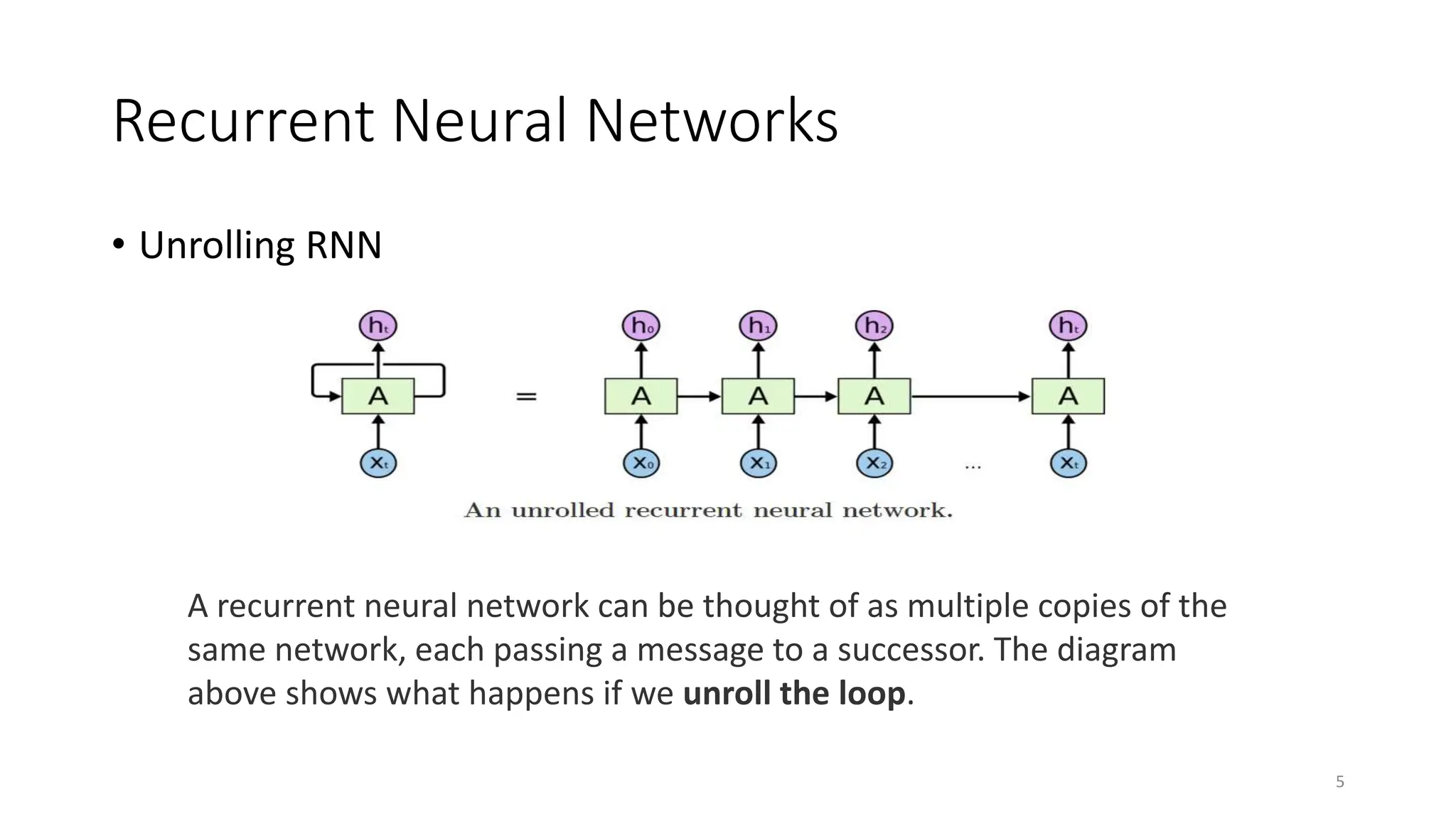
Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are designed to process sequential data like time series and text. RNNs include loops that allow information to persist from one step to the next to model temporal dependencies in data. However, vanilla RNNs suffer from exploding and vanishing gradients when training on long sequences. Long short-term memory (LSTM) and gated recurrent unit (GRU) networks address this issue using gating mechanisms that control the flow of information, allowing them to learn from experiences far back in time. RNNs have been successfully applied to many real-world problems involving sequential data, such as speech recognition, machine translation, sentiment analysis and image captioning.

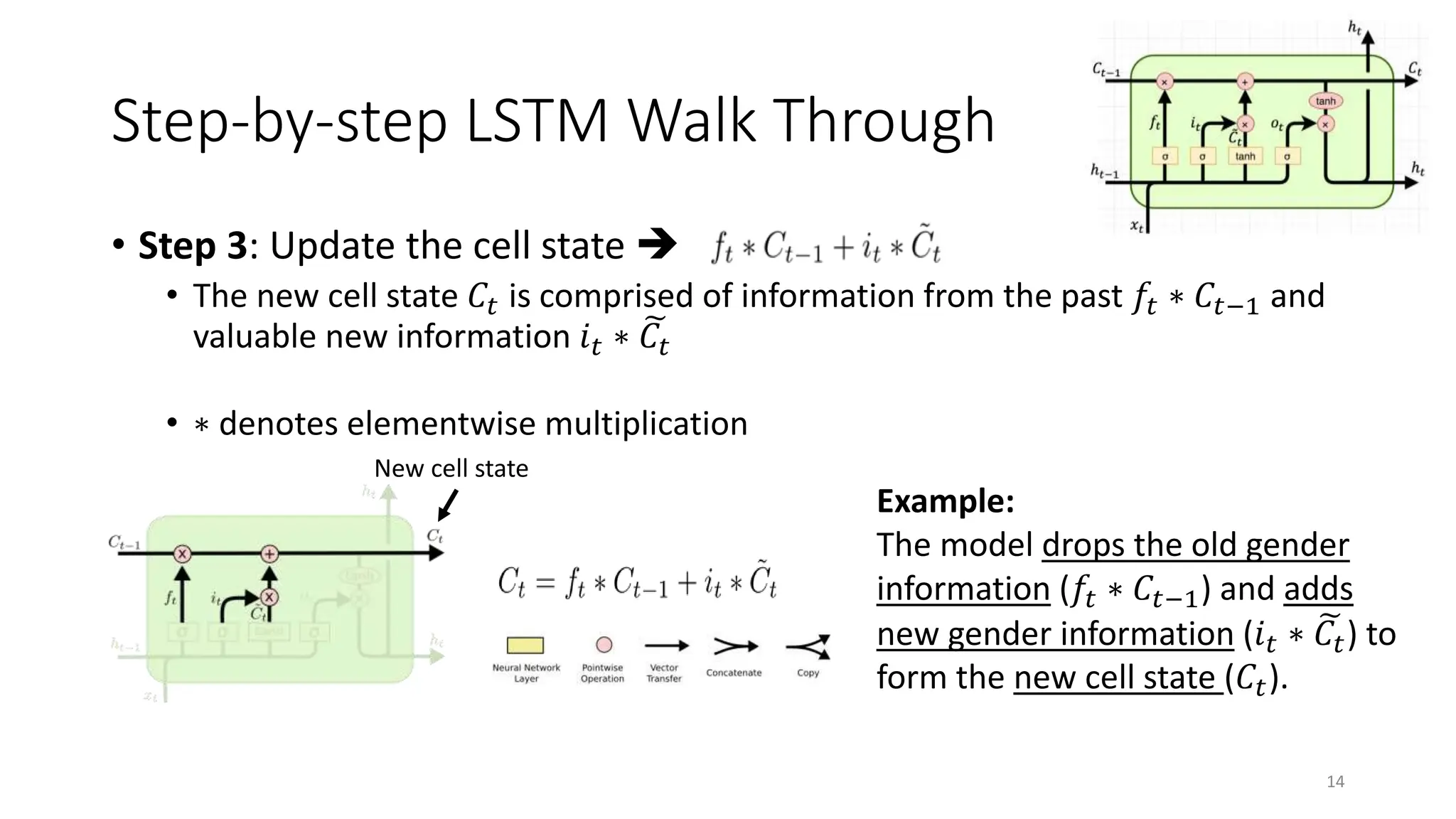
![Step-by-step LSTM Walk Through
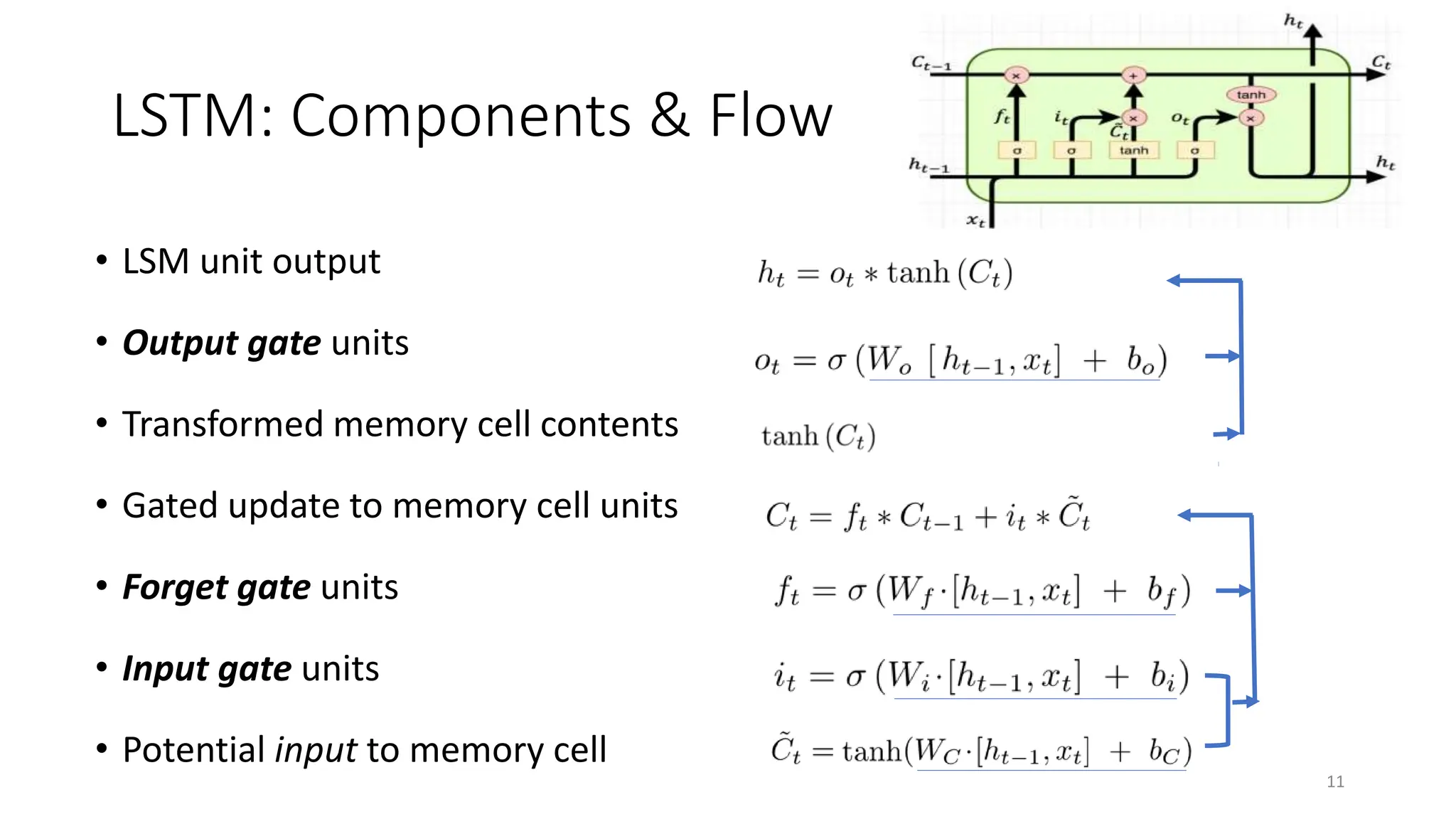
• Step 1: Decide what information to throw away from the cell state
(memory)
• The output of the previous state ℎ𝑡−1 and the new information 𝑥𝑡 jointly
determine what to forget
• ℎ𝑡−1 contains selected features from the memory 𝐶𝑡−1
• Forget gate 𝑓𝑡 ranges between [0, 1]
12
Forget gate
Text processing example:
Cell state may include the gender
of the current subject (ℎ𝑡−1).
When the model observes a new
subject (𝑥𝑡), it may want to forget
(𝑓𝑡 → 0) the old subject in the
memory (𝐶𝑡−1).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5rnnandlstm-240312104154-16f58e6f/75/RNN-and-LSTM-model-description-and-working-advantages-and-disadvantages-12-2048.jpg)
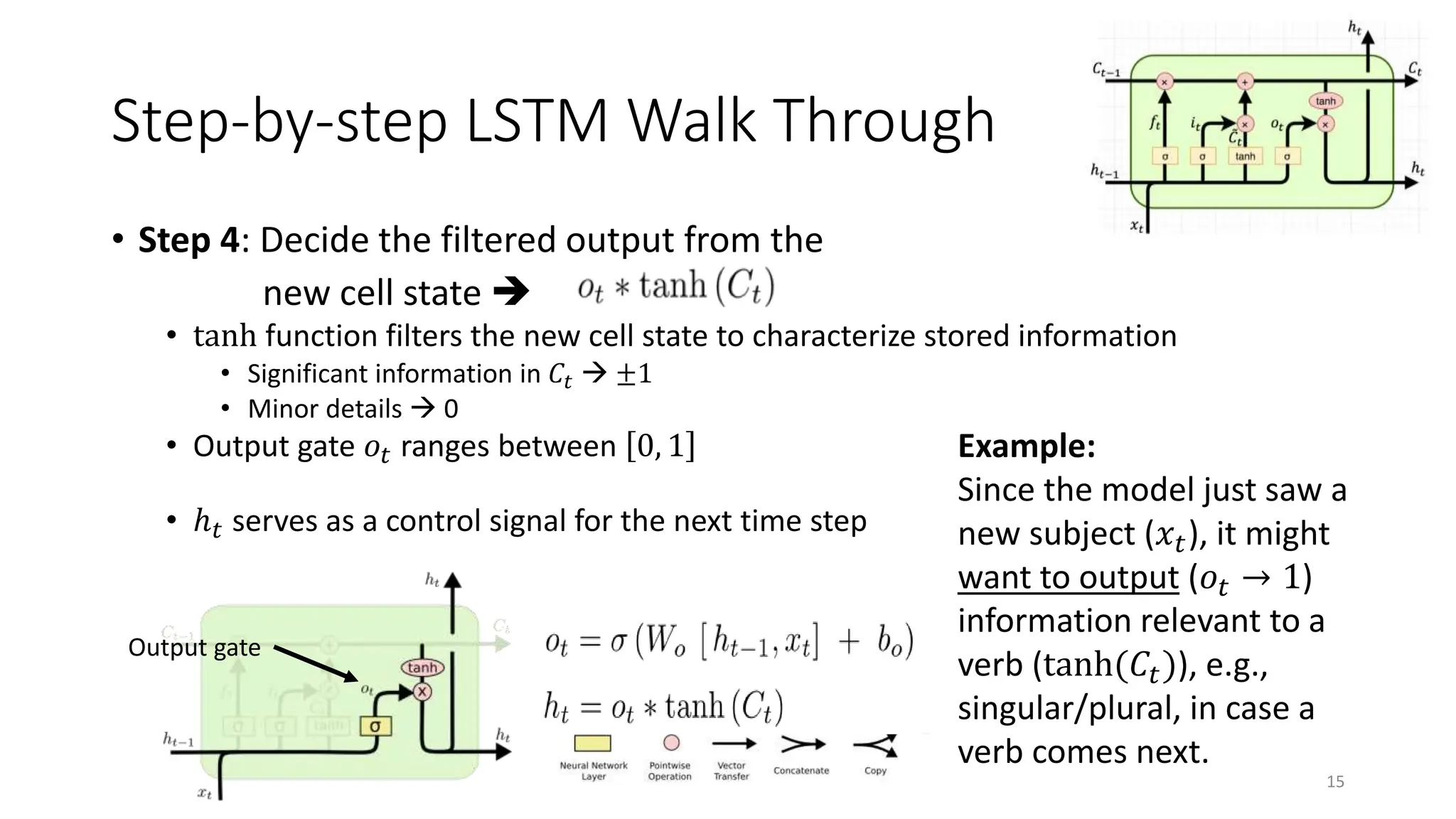
![Step-by-step LSTM Walk Through
• Step 2: Prepare the updates for the cell state
from input
• An alternative cell state 𝐶𝑡 is created from the new information 𝑥𝑡 with the
guidance of ℎ𝑡−1.
• Input gate 𝑖𝑡 ranges between [0, 1]
13
Input gate Alternative
cell state
Example:
The model may want to add
(𝑖𝑡 → 1) the gender of new
subject (𝐶𝑡) to the cell state to
replace the old one it is
forgetting.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5rnnandlstm-240312104154-16f58e6f/75/RNN-and-LSTM-model-description-and-working-advantages-and-disadvantages-13-2048.jpg)