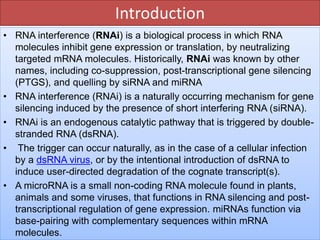
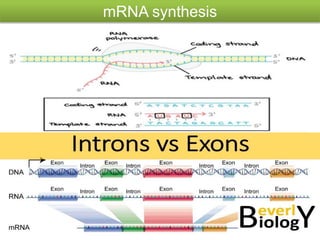
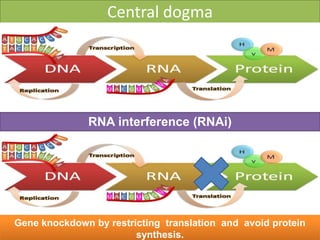
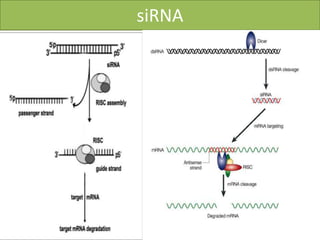
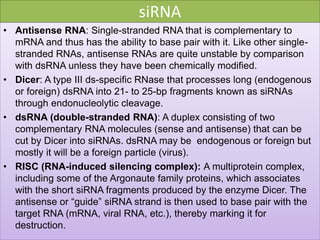
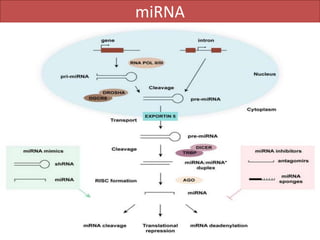
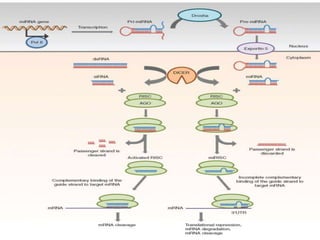
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process where RNA molecules inhibit gene expression by neutralizing mRNA. It is triggered by double-stranded RNA and functions through two main types: small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). siRNAs are produced by an enzyme called Dicer from long double-stranded RNAs and incorporated into an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to degrade mRNA. miRNAs are endogenous single-stranded non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by blocking translation or destroying mRNA through base-pairing.