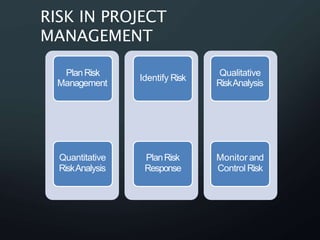
Risk management is the process of identifying and mitigating risks that may affect a project. It includes planning risk management, identifying risks, analyzing risks qualitatively and quantitatively, planning risk responses, maintaining a risk register, and monitoring and controlling risks. The key benefits of risk management are reducing the negative impacts of risks, increasing the probability of positive outcomes, and effectively allocating resources to address risks.