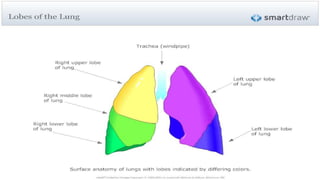
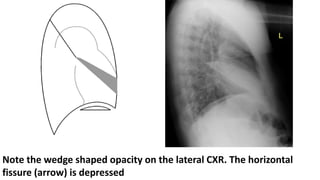
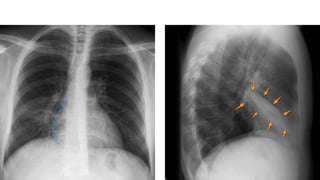
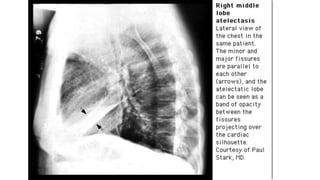
Chronic collapse of the right middle lobe, known as right middle lobe syndrome, is most commonly seen in elderly women. On chest x-rays, chronic collapse presents with subtle findings such as a triangular opacity pointing laterally where the normal horizontal fissure would be located and blurring of the right heart border. CT scans more clearly show the "tilted ice cream cone" appearance of the collapsed right middle lobe pressing against the heart. The document provides details on the radiographic presentation and characteristics of chronic right middle lobe collapse.