1) Lobar collapse refers to the collapse of an entire lobe of the lung, which can be caused by obstruction of the supplying bronchus.
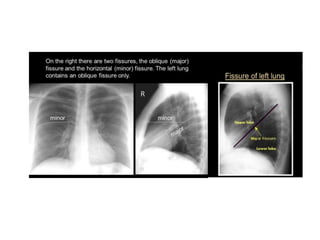
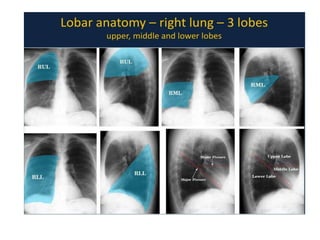
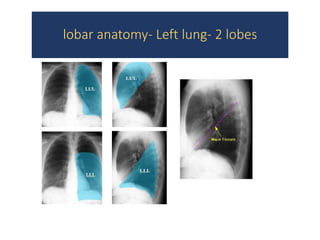
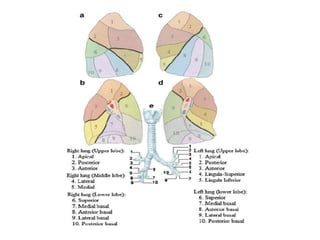
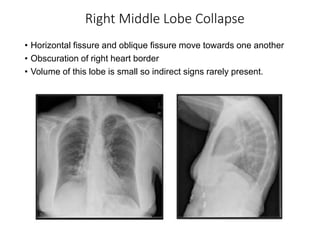
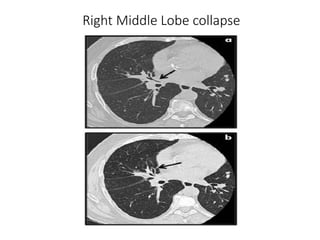
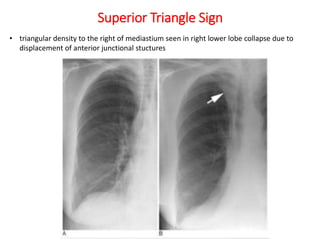
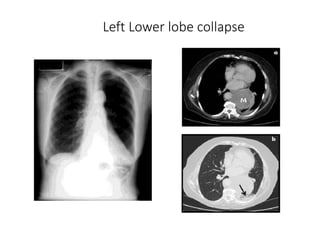
2) Signs of lobar collapse include shift of fissures, crowding of pulmonary vessels, hemithorax elevation, mediastinal shift, and compensatory hyperinflation of normal lobes.
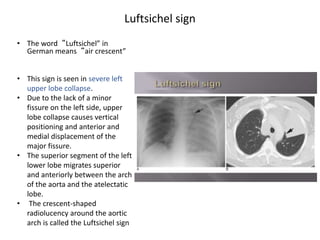
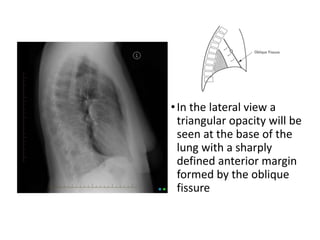
3) Collapse of different lung lobes shows characteristic radiographic findings, such as Golden's S sign for right upper lobe collapse and the Luftsichel sign for left upper lobe collapse.