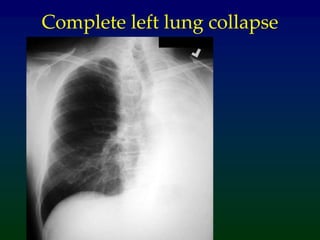
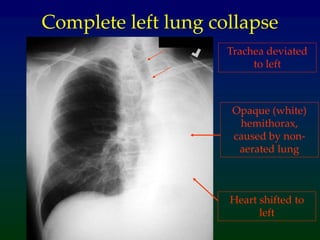
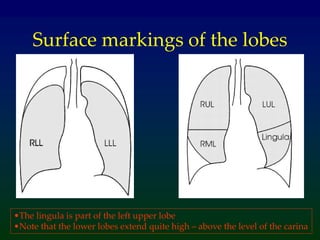
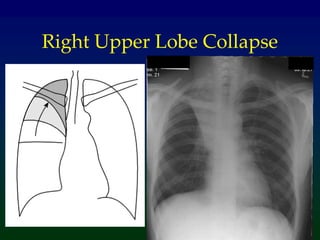
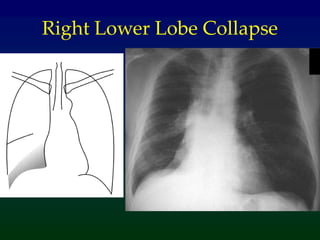
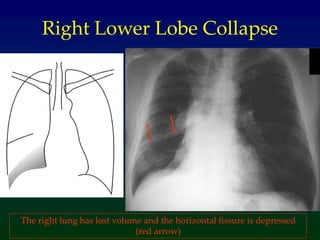
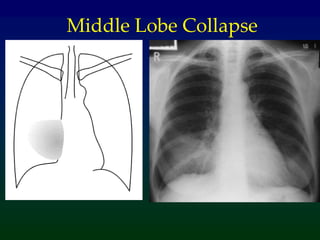
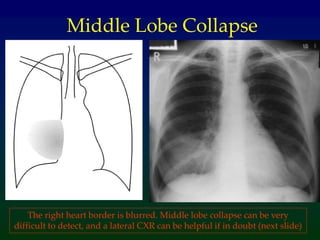
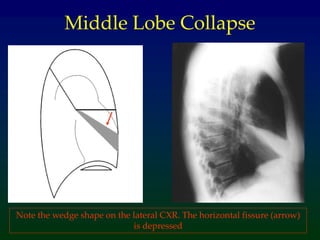
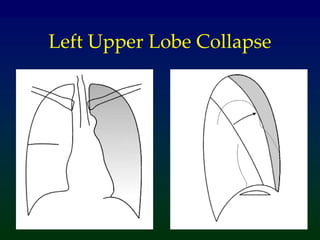
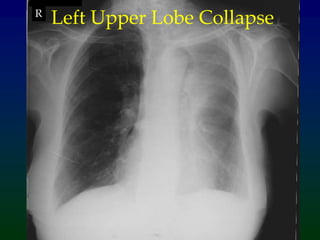
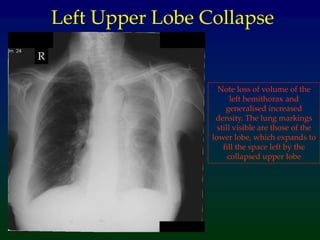
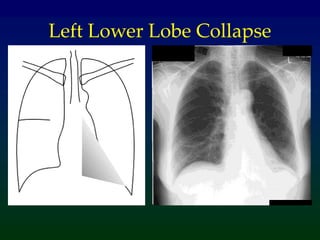
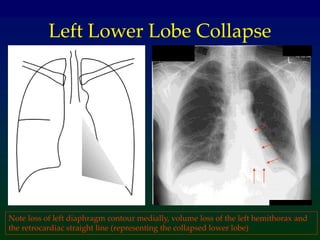
Atelectasis refers to lung collapse with loss of internal air, affecting parts of a lung or the entire lung, with subsegmental atelectasis being the most common. Causes include bronchogenic carcinoma, asthma, and foreign body aspiration, with specific chest X-ray features indicating collapse, such as tracheal displacement and increased density. Diagnosis requires assessing volume loss and the movement of surrounding structures, with lung cancer being the most common cause in adults.