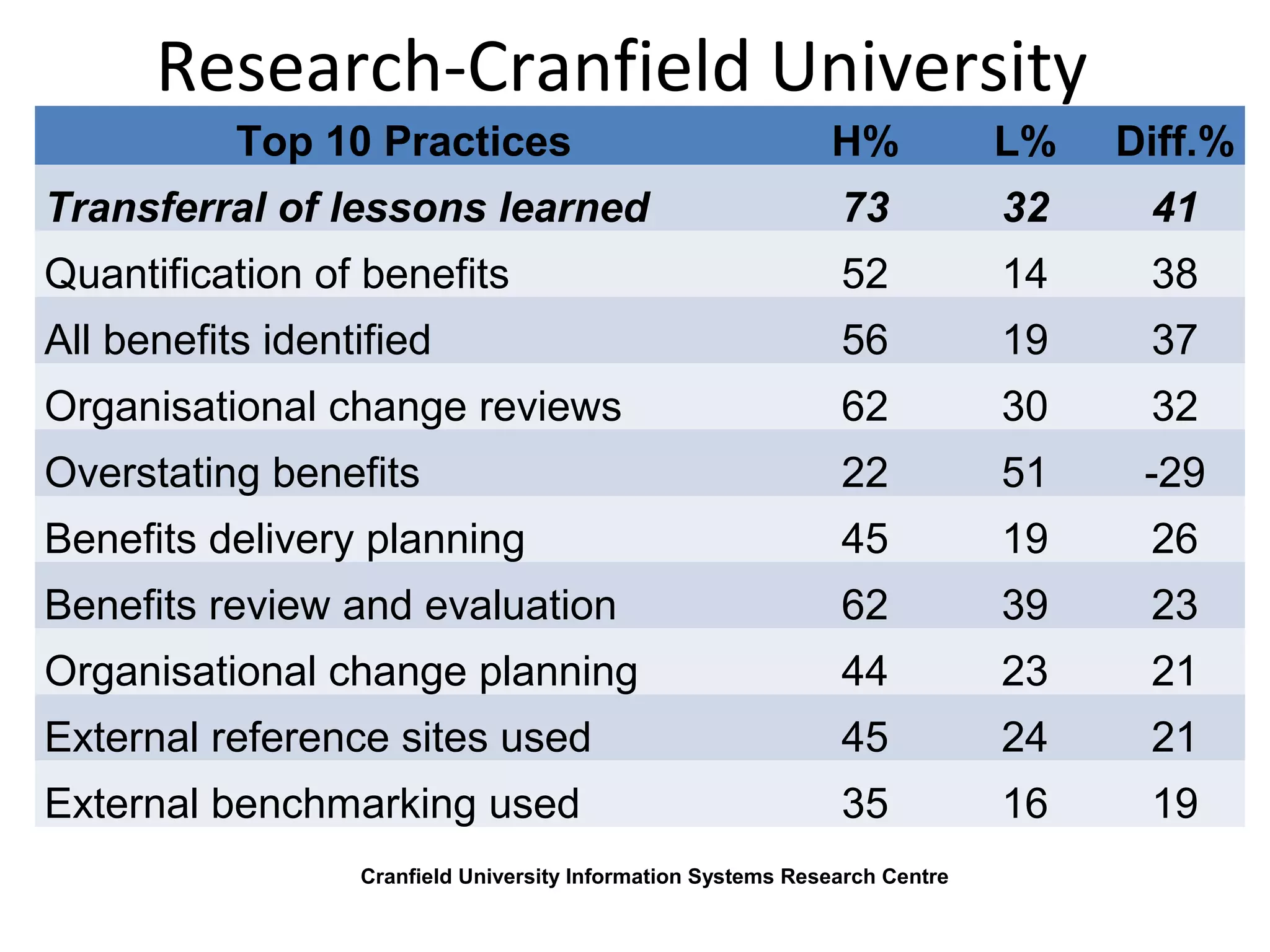
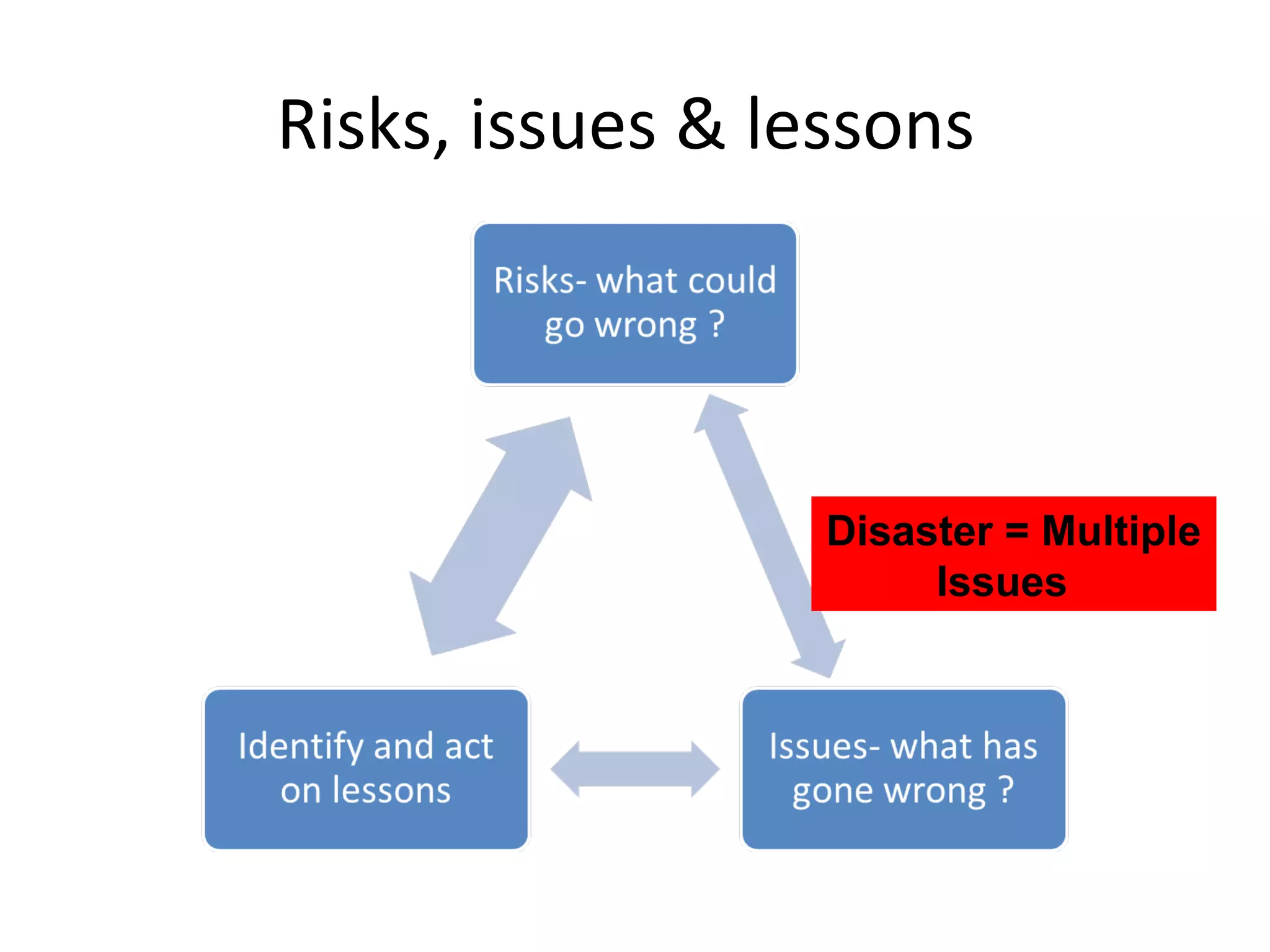
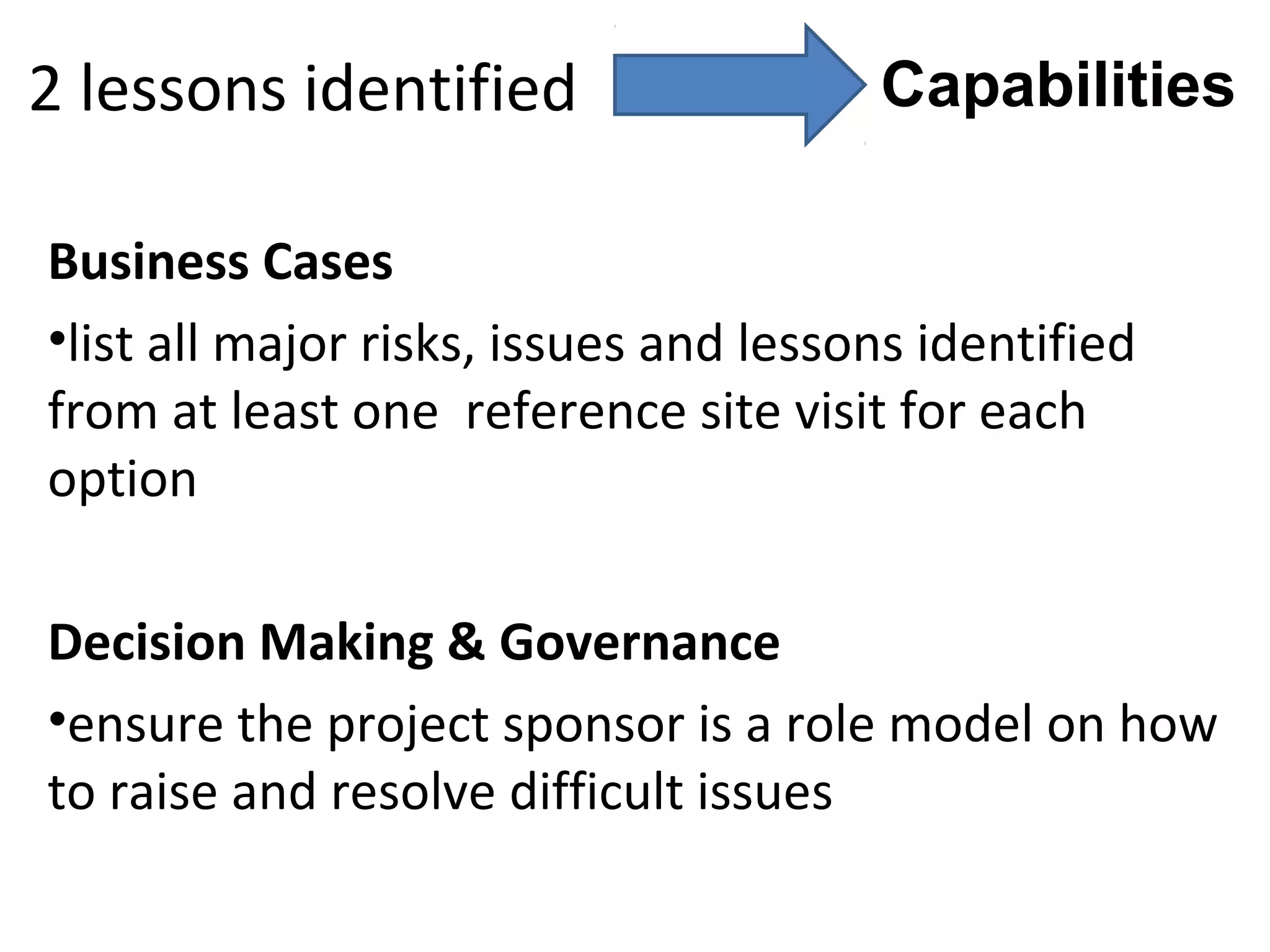
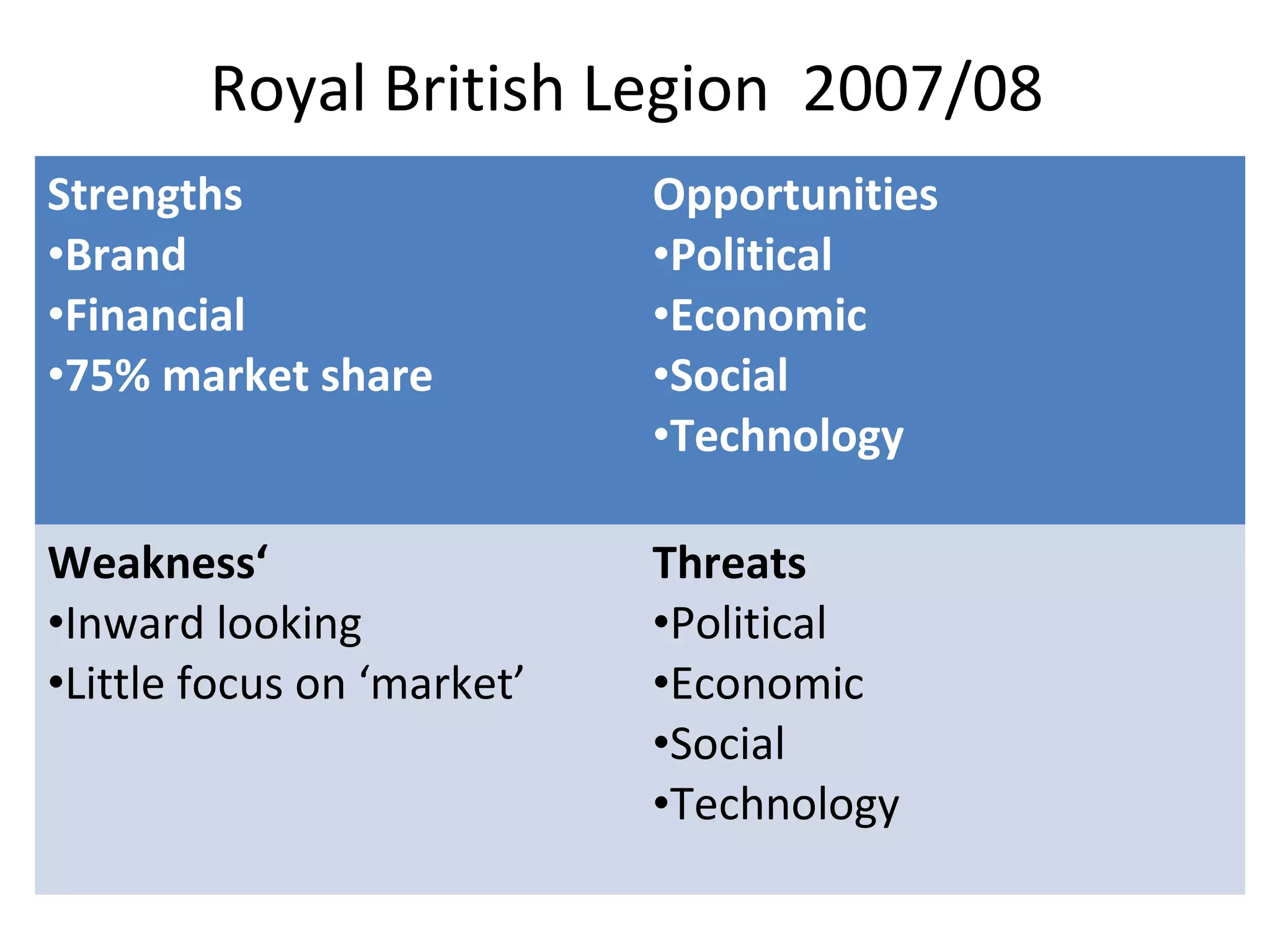
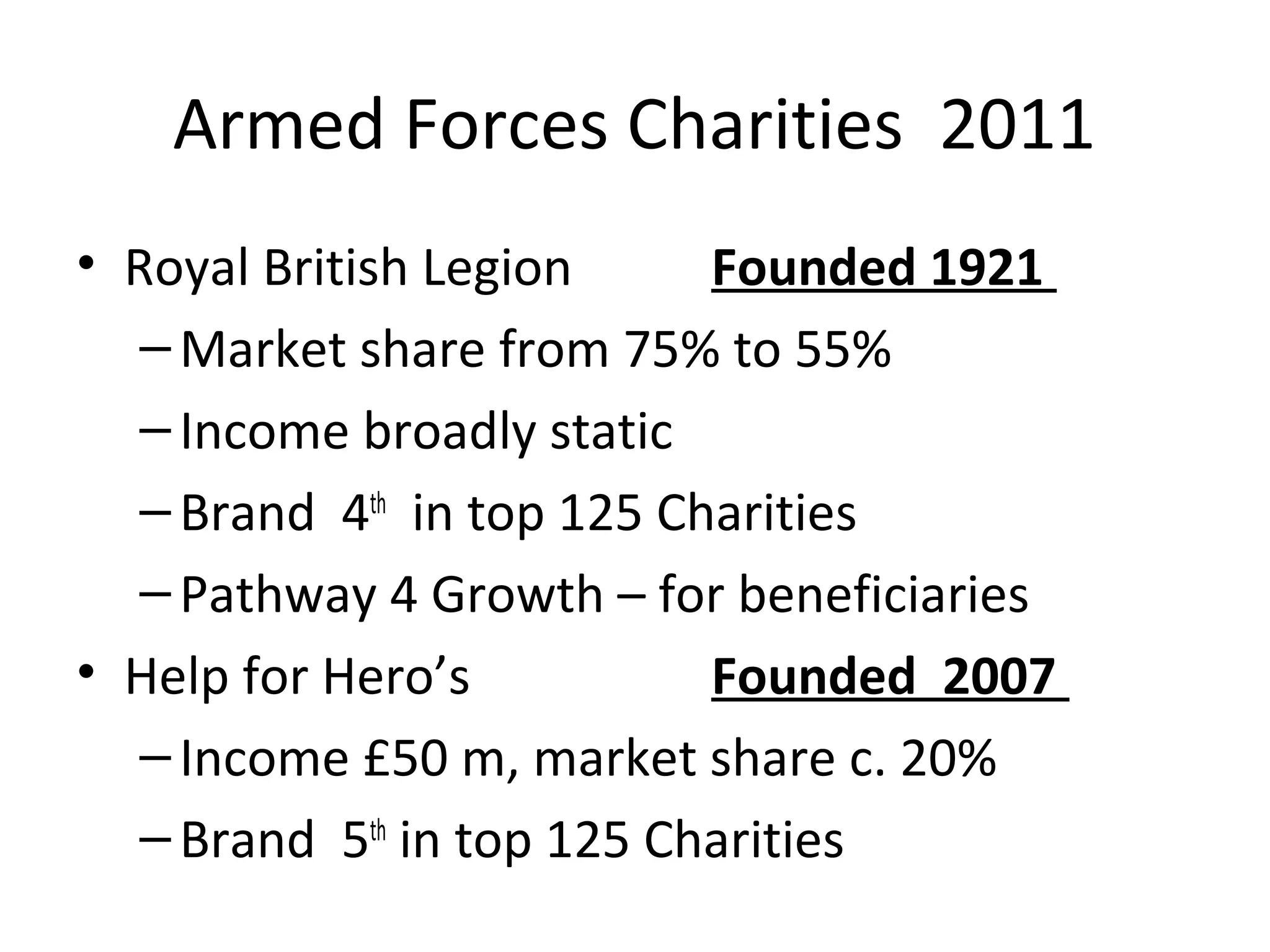
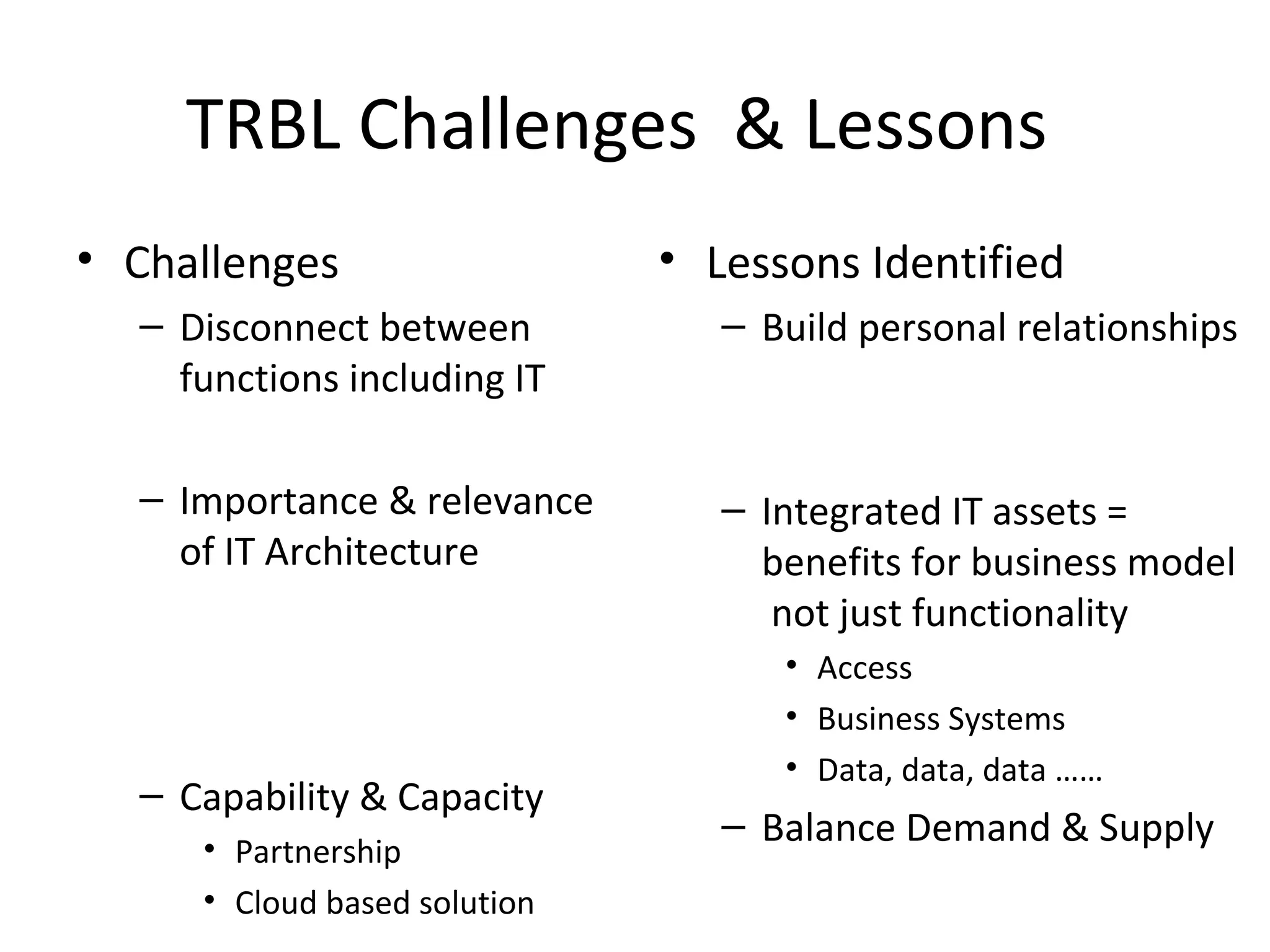
This document discusses business IT investment risks and lessons learned from past projects. It identifies 10 best practices for successful IT investments based on research, including quantifying benefits and identifying all stakeholders. Two key lessons are to list all risks and issues from reference sites for each option, and ensure project sponsors address difficult issues. The document also discusses challenges faced by armed forces charities in a changing environment and how the Royal British Legion's business model and operating model are transitioning in response.