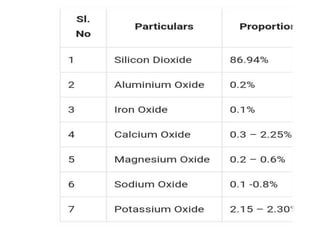
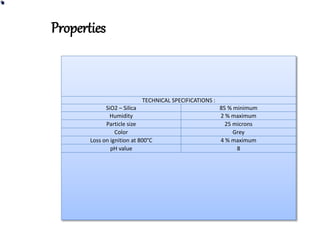
Rice husk ash (RHA) is produced when rice husks are burned in boilers. Approximately 25% of rice husk mass becomes RHA. RHA has a high silica content and fineness similar to or finer than cement. Concrete containing 10-20% RHA as a partial cement substitute has superior performance characteristics compared to normal concrete. RHA is estimated to be produced at 70 million tons annually worldwide and has applications in high performance concrete, insulation, and construction due to its pozzolanic properties.