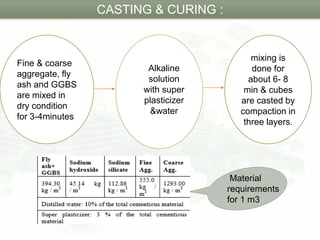
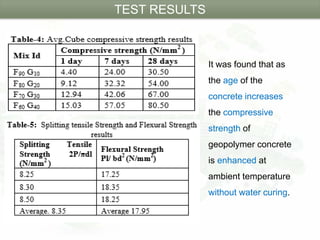
This document summarizes a research paper on geopolymer concrete, an eco-friendly construction material. It describes geopolymer concrete as a cementless material made by activating fly ash and slag using alkaline liquids instead of Portland cement. The objectives of the study were to produce a carbon dioxide emission-free cementitious material and evaluate the compressive strength of mixes with varying fly ash and GGBS contents. The results showed that geopolymer concrete gained strength within 24 hours at ambient temperature without water curing, and mixes with higher GGBS content achieved greater compressive strength, with the F60G40 mix attaining the maximum of 80.50N/mm2.