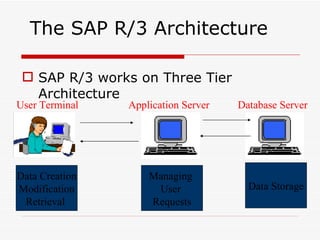
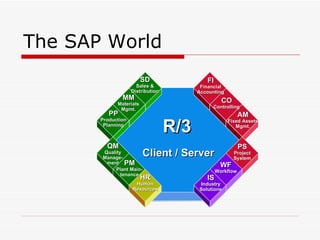
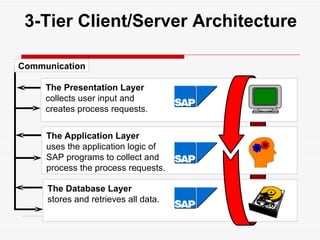
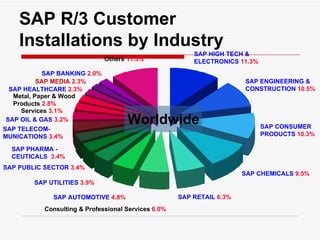
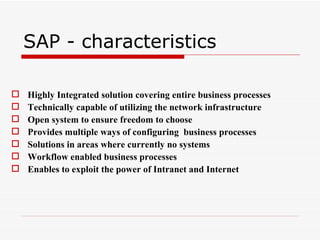
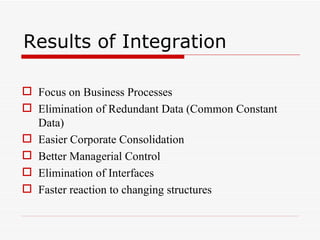
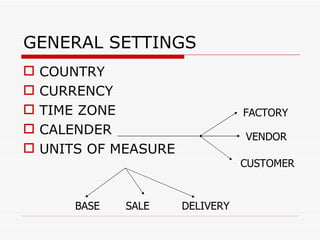
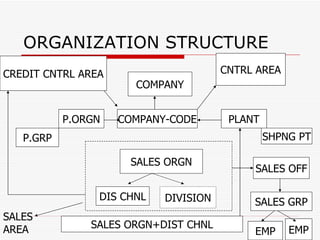
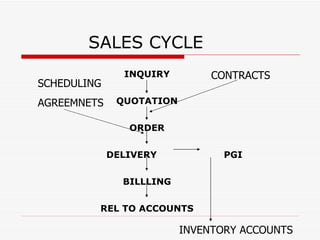
This document provides an overview of SAP Sales and Distribution (SD) module. It begins with introductions and definitions of key concepts like ERP, resources, and planning. It then discusses the SD module in detail including configuration settings, master data, basic functions like pricing and partner determination, shipping, billing, and special functionalities. The document aims to equip the reader with foundational knowledge of SAP SD.