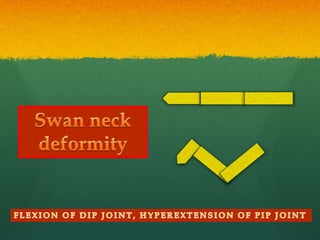
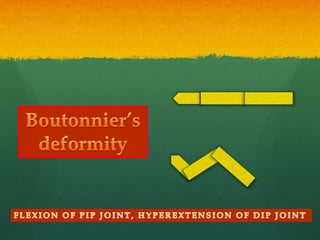
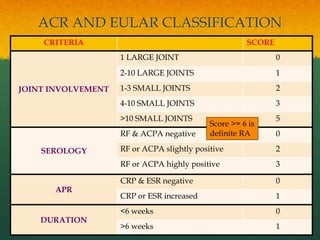
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that results in joint damage and physical disability. It most commonly involves the small symmetrical joints of the hands and feet. Extra-articular manifestations can include fatigue, weight loss, lung and heart involvement. Risk factors include family history, smoking, and female sex. Treatment involves rest, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs like methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine, steroids, and sometimes biological DMARDs or surgery.