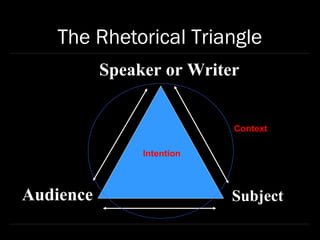
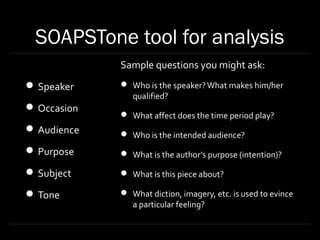
Rhetoric is defined as observing the available means of persuasion in a given situation. Speakers take into account their understanding of the audience and subject as well as their own intentions when communicating. The document outlines tools like SOAPSTone for analyzing rhetorical elements such as the speaker, audience, purpose, subject, and tone of a piece of writing or speech.