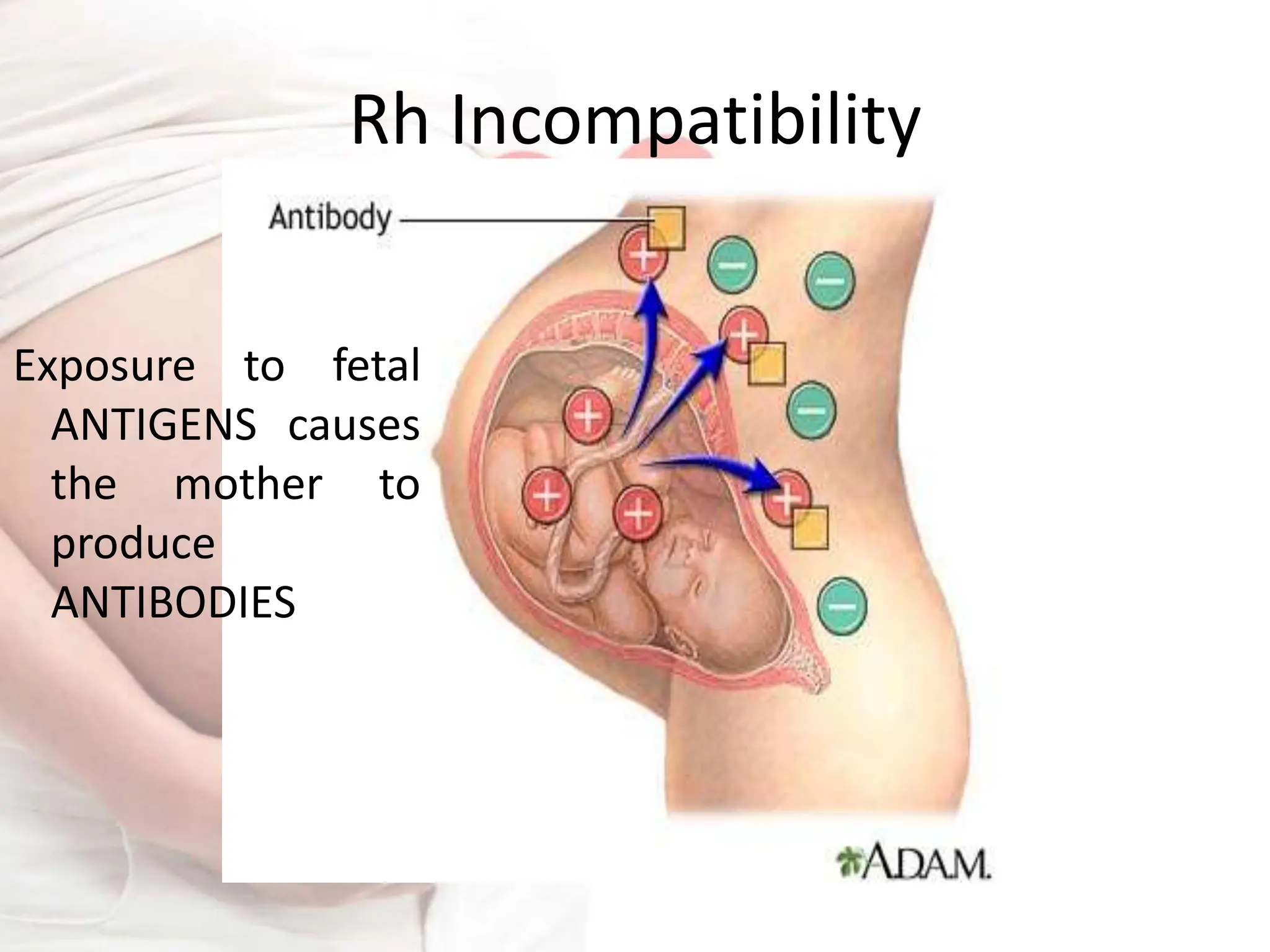
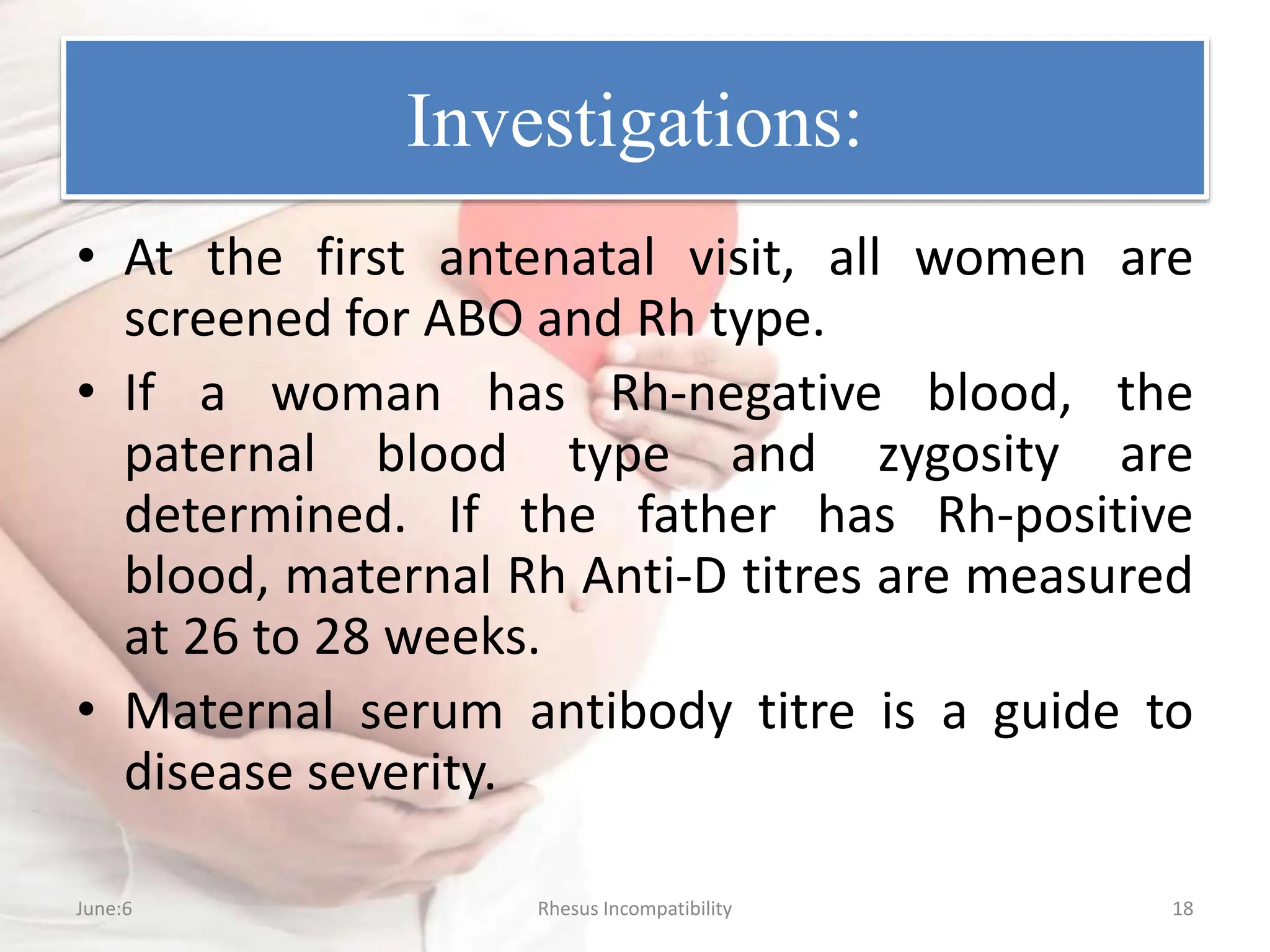
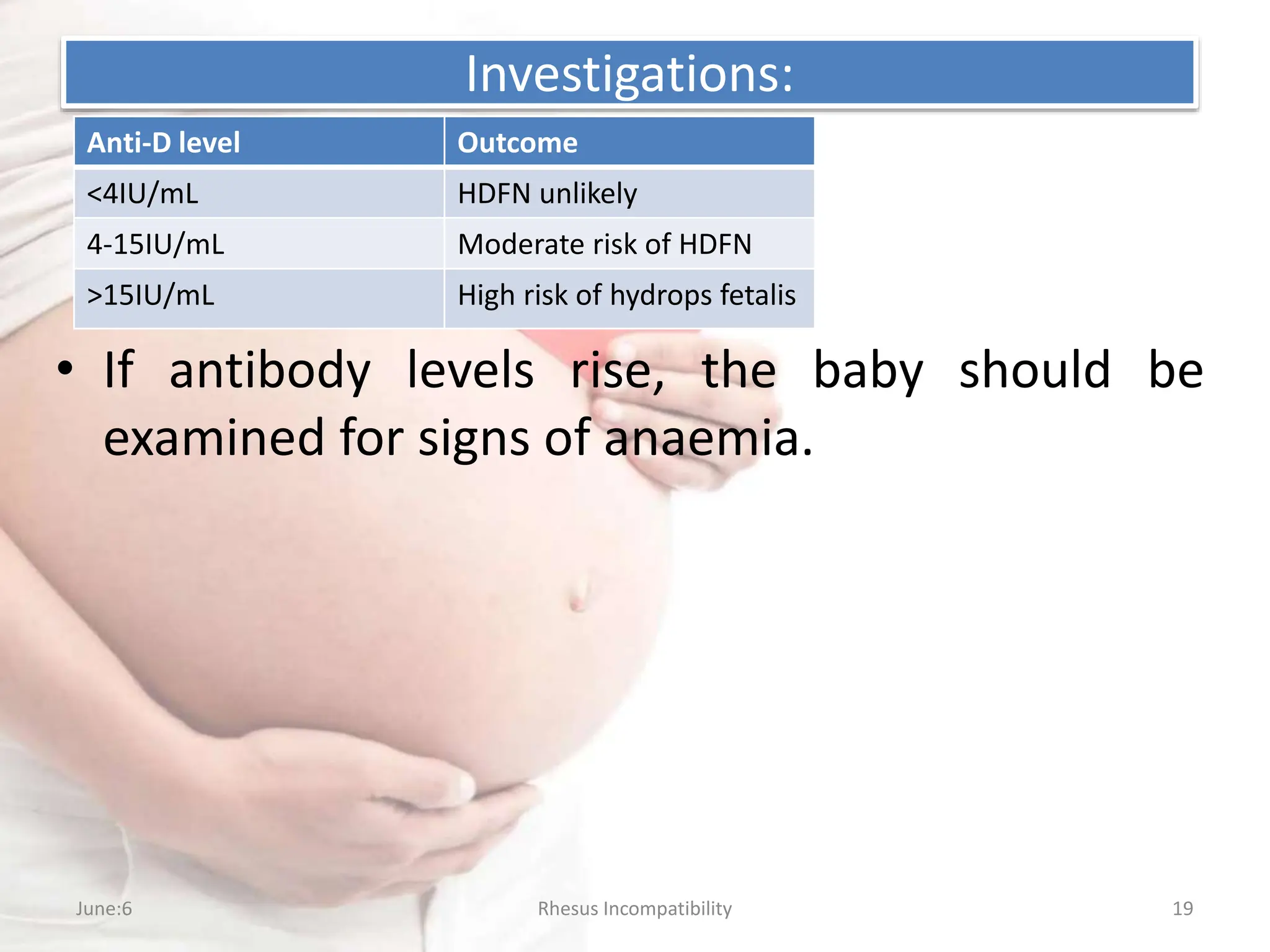
Rh incompatibility occurs when a mother has Rh-negative blood and the fetus has Rh-positive blood. This can lead to hemolytic disease in subsequent pregnancies as the mother's immune system produces antibodies against the Rh-positive fetal blood cells. Key aspects of management include Rh immunoglobulin injections for Rh-negative mothers after pregnancy events or delivery of an Rh-positive baby to prevent sensitization, monitoring of sensitized mothers and treatment of affected fetuses or newborns which may include intrauterine transfusions, induction of early delivery, exchange transfusions, and phototherapy.