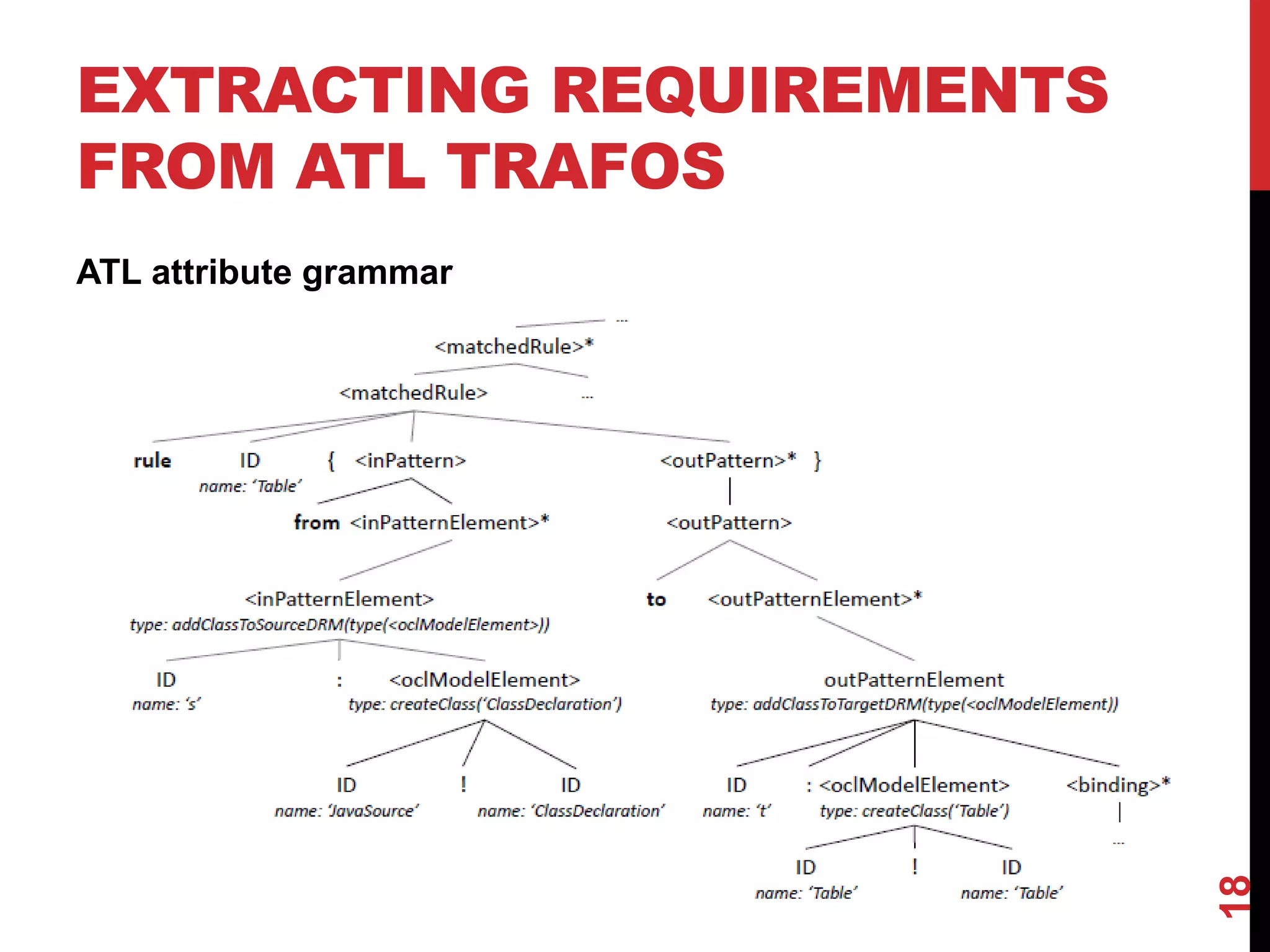
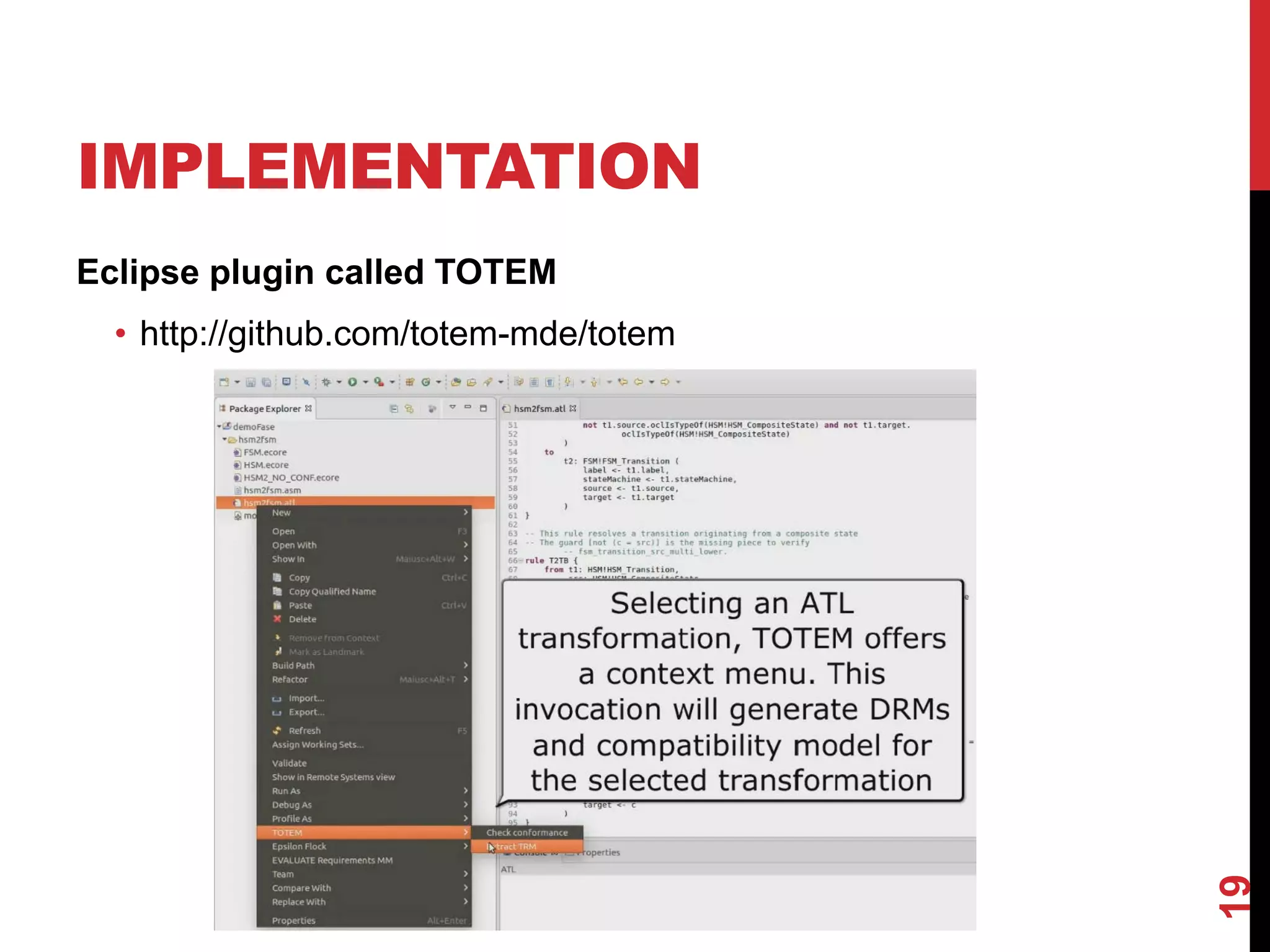
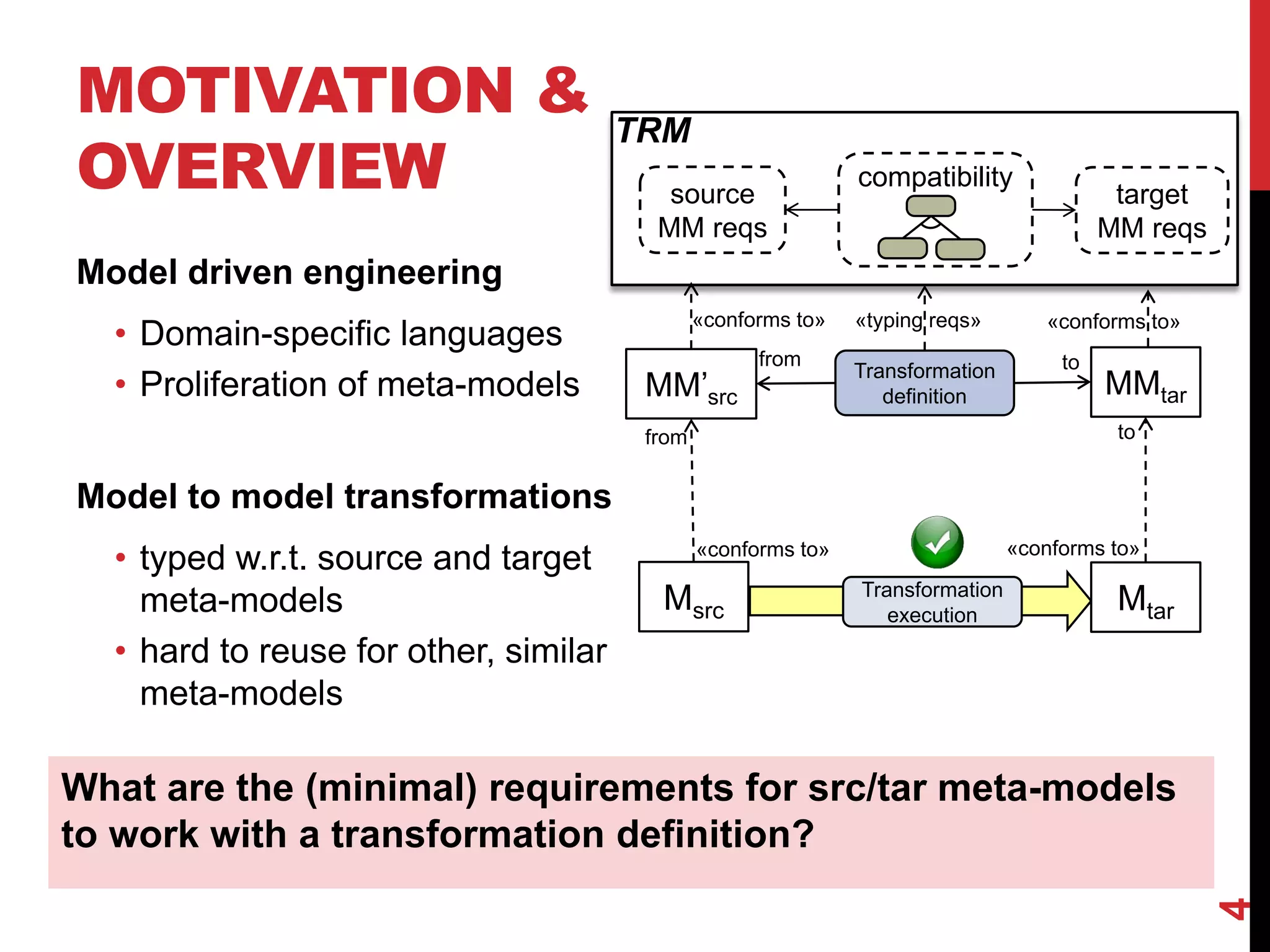
This document presents an approach for reusing model transformations through the extraction of typing requirements models (TRMs) from transformations. TRMs characterize the minimal requirements that source and target meta-models must satisfy for a transformation to be well-typed. The approach extracts TRMs from ATL transformations through an attribute grammar. Meta-models can then be checked for conformance to the TRMs to determine if a transformation can be reused. An evaluation of the approach on four transformations showed that it achieved high precision and recall in checking over 2,000 mutated meta-models for conformance.







![DRM META-MODEL
11
mandatoryAllowed: boolean
subsAllowed: boolean
isAbstract: UBoolean
Feature
name: String[1]*
feats
Reference
Cardinality
Number
value: int
allowLess: boolean
allowMore: booolean
Any
Cardinality
Many
min 1
max 1
Attribute
* targets
DataType
Numeric
Real Integer
StringAny
DataType
Enum Literal
name: String[1]name: String[0..1]
*
literals
dtype1
ancs
*
antiancs *
FeatureType
*
isOrdered: UBoolean
isUnique: UBoolean
<<enum>>
UBoolean
True
False
Any
Anonymous
Class
types
INVARIANTS:
context Feature inv: not self.min.oclIsTypeOf(Many)
Boolean
Class
Named
Class
name: String](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fasereqmodels-170428191518/75/ReusingMT-11-2048.jpg)