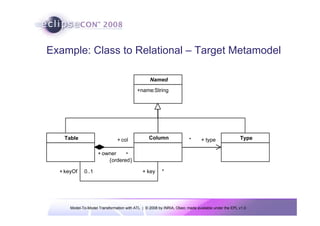
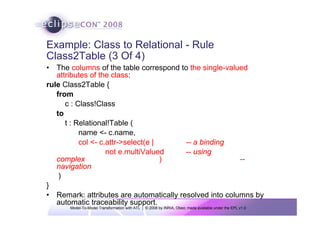
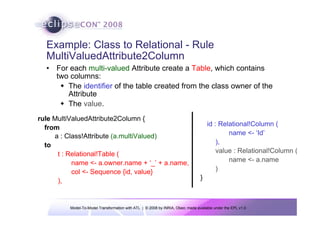
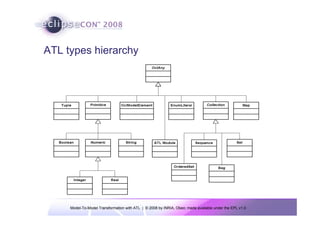
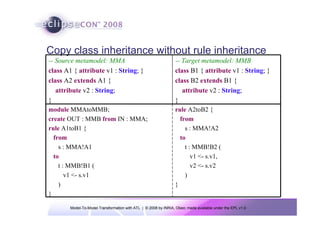
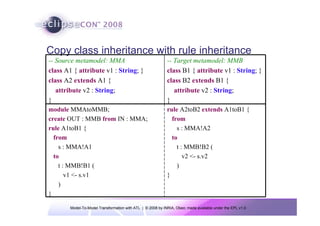
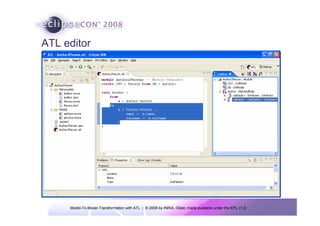
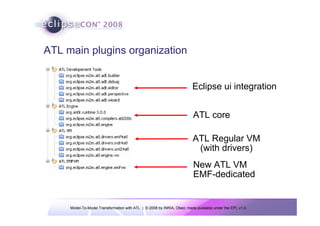
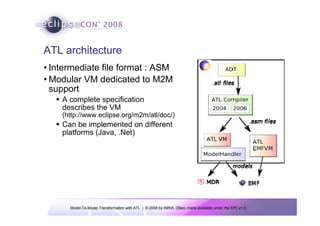
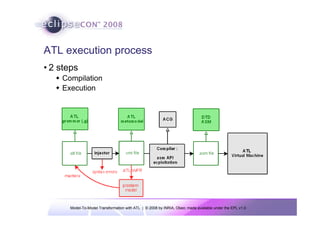
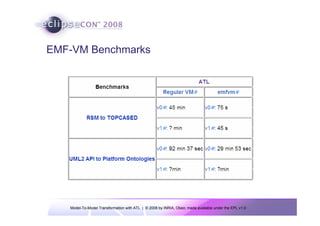
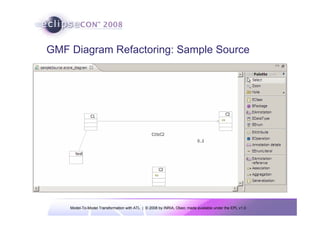
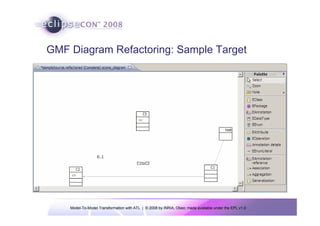
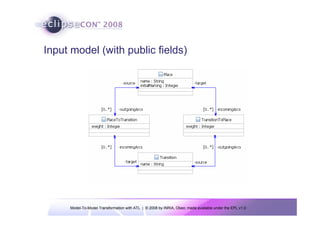
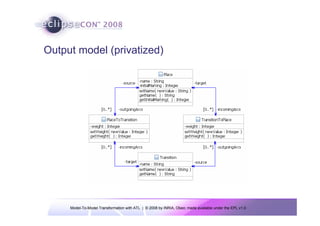
The document discusses model-to-model (M2M) transformation using the ATLAS Transformation Language (ATL). It provides an overview of ATL, including its history, community resources, and programming style. The document describes how ATL transformations work, including the use of declarative rules to match source patterns and create target patterns, and imperative rules that can contain declarative patterns and action blocks. Examples of ATL rules and transformations are also presented.