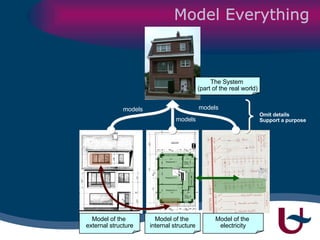
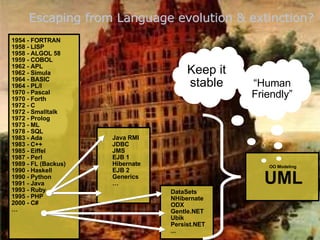
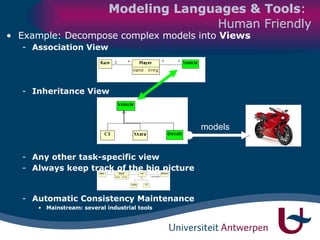
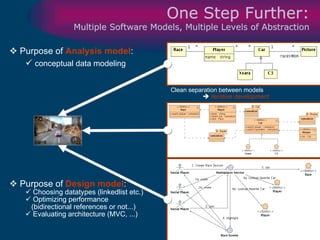
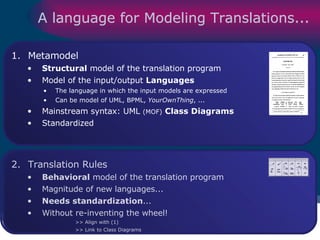
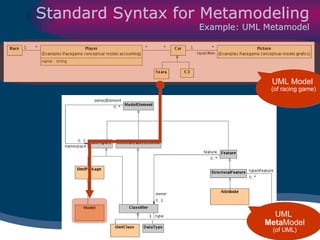
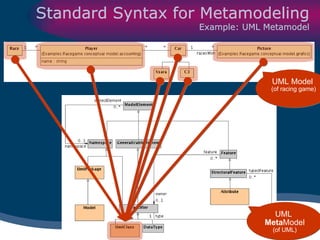
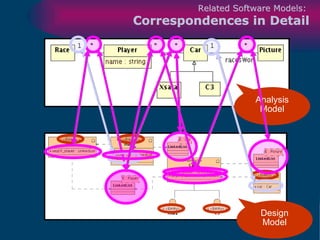
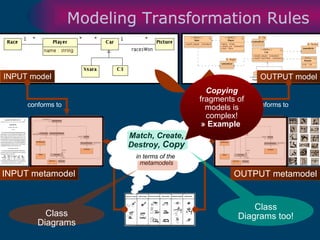
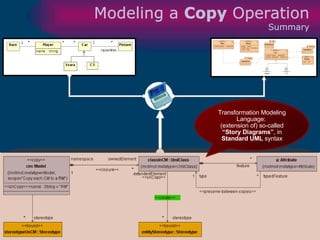
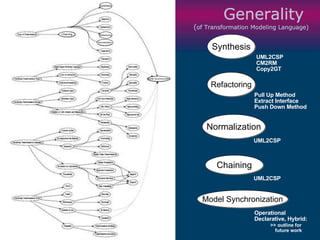
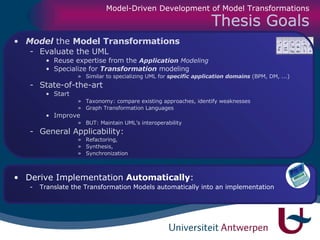
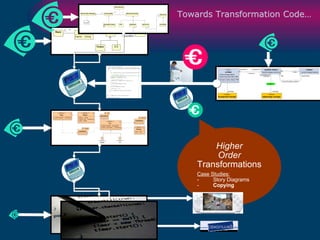
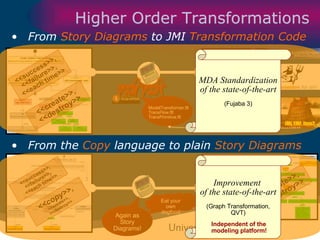
The document discusses model-driven development (MDD) of model transformations, emphasizing the importance of automating transformations in software development to improve efficiency and reduce errors. It outlines various goals, methodologies, and principles for modeling transformations, while also noting the need for standardization and interoperability of modeling languages like UML. The thesis argues for a systematic approach to transforming models and highlights the applicability of these methods in various domains of software engineering.