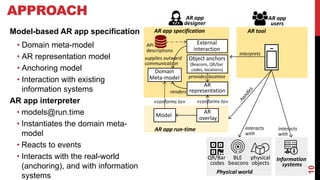
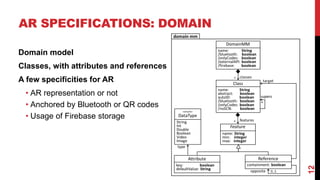
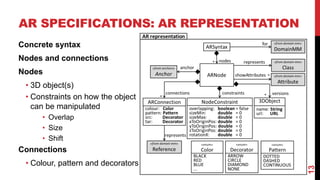
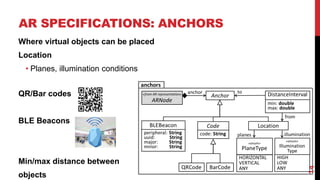
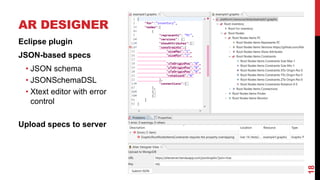
This document describes a model-driven approach to building augmented reality (AR) applications. Key points:
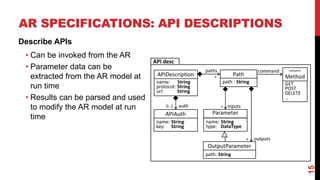
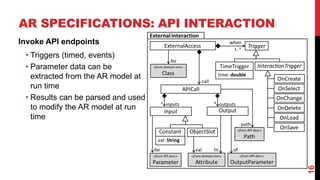
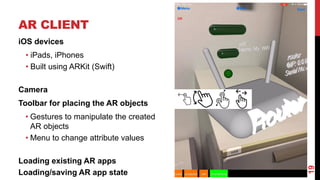
- AR applications are specified using models that describe the domain, AR representation, object anchoring using techniques like QR codes and beacons, and interaction with external APIs.
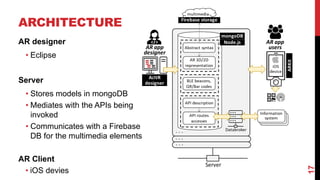
- An AR interpreter renders the virtual objects based on the models and allows interaction in the physical world.
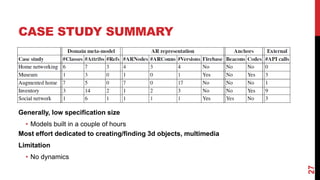
- The approach was evaluated through case studies of AR apps for networking, museums, home design, inventory, and social media. A user study found the AR apps to have good usability.
- Future work includes adding physics, collaborative editing, migrating the designer to the web, and more user studies.