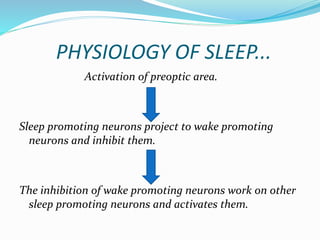
This document defines rest and sleep, describes the physiology and stages of sleep, and discusses factors affecting sleep and common sleep disorders. Sleep is defined as a state of rest accompanied by altered consciousness and inactivity. There are two types of sleep - non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep consists of 4 stages that progress from light to deep sleep. REM sleep is characterized by increased brain activity and vital signs but decreased muscle activity. Factors like environment, lifestyle, and drugs can impact sleep quality and disorders like insomnia, sleep apnea, and nightmares are also discussed. Nursing measures to promote sleep are provided.