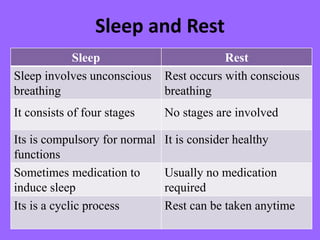
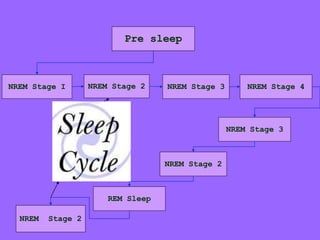
This document discusses sleep and rest patterns. It defines sleep and rest, compares their characteristics, and discusses the two types of sleep - NREM and REM sleep. The four stages of NREM sleep and characteristics of REM sleep are outlined. Factors affecting sleep, common sleep disorders, functions of sleep, and nursing management of patients' sleep are also covered. Nursing management involves assessing, diagnosing, planning, implementing, teaching, and evaluating patients to promote healthy sleep.