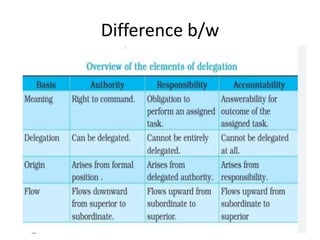
The document discusses the concepts of authority, responsibility, and accountability. It defines them as follows:
- Authority is the right to give orders or instructions.
- Responsibility is the obligation to achieve objectives.
- Accountability is the obligation to report to higher authorities on the discharge of responsibilities.
It explains that accountability flows upward, while responsibility is assigned downward. Authority and responsibility must be aligned, and accountability relies on the delegation of authority and responsibility.