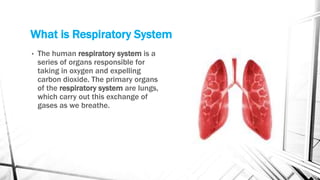
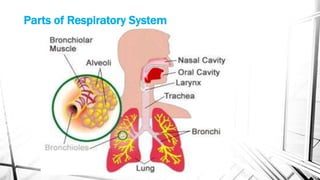
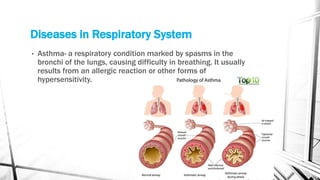
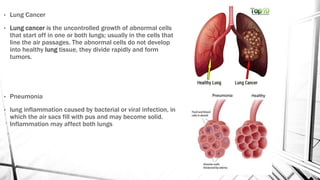
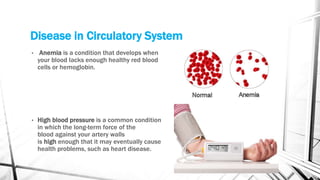
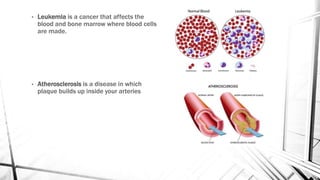
The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body and removes carbon dioxide. It includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and lungs. The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body using the heart, arteries, veins and capillaries. It has two circuits - pulmonary and systemic. Diseases can affect both systems like asthma, pneumonia, anemia and atherosclerosis.