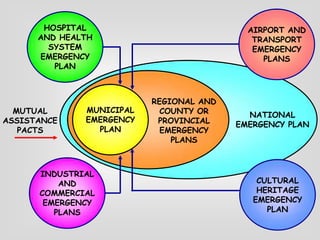
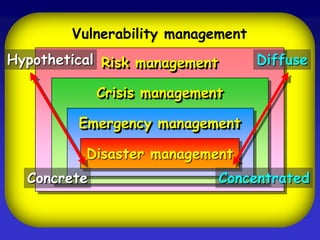
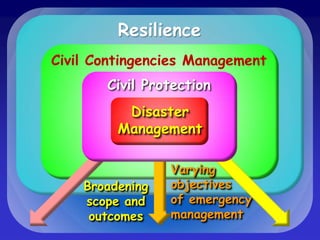
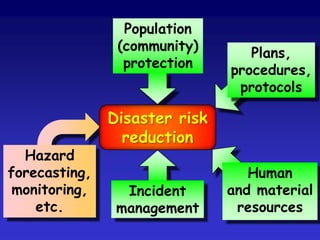
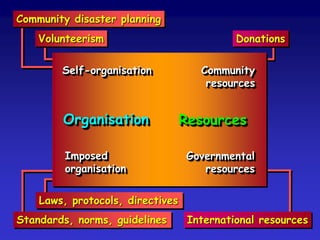
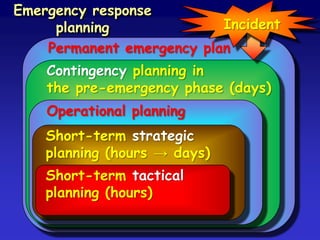
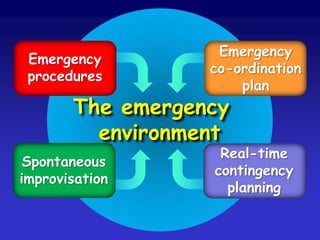
This document discusses the concepts of resilience and vulnerability in emergency response systems. It defines resilience as the ability to recover readily from shocks through a combination of attitude, preparedness, and redundancy. Vulnerability is the potential for harm and is inversely related to resilience. The key aspects of resilient emergency response systems identified are adequate training and resources, robust collaborative command structures, inclusive participation, adaptable emergency plans, and redundant communications. A sustainable emergency response system is locally supported, continuously developing, and based on emergency planning that is applied flexibly and serves as an everyday function.

![Resilience [Resiliency]:definition: readily recovering from shock, buoyantthe term is derived from rheology, the science of the deformationofmatteraswithmaterials, so with society:aimfor the optimum combinationofabilitytoresist and absorbshocksresilience is an amalgam of attitude, preparedness and redundancy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/resilienceandvulnerability-100528054011-phpapp01/85/Resilience-and-vulnerability-2-320.jpg)





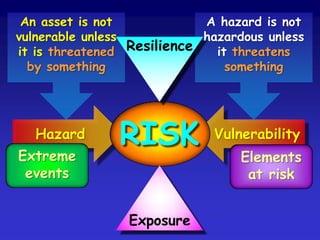

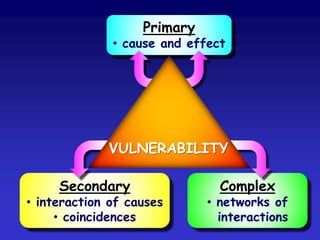
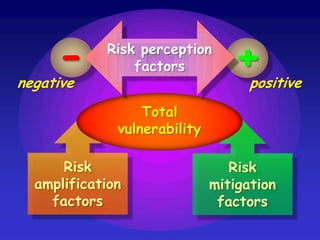




![(Hazard x Vulnerability x Exposure)Resilience= Risk[ -> Impact -> Response]....alternatively:-Hazard x (Vulnerability / Resilience)[x Exposure]= Risk[ -> Impact -> Response]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/resilienceandvulnerability-100528054011-phpapp01/85/Resilience-and-vulnerability-22-320.jpg)