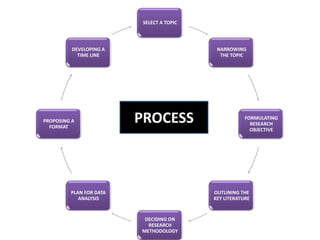
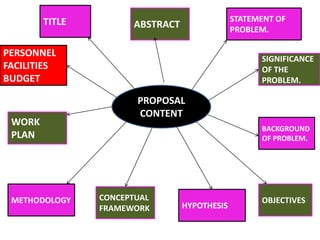
This document provides guidance on writing a research proposal in 3 sections. The introduction defines a research proposal and discusses its purpose. The main section outlines the key components of a proposal, including the title, abstract, statement of problem, objectives, methodology, work plan, personnel, facilities, budget, and format. The conclusion emphasizes doing thorough planning and writing the proposal in a clear, concise manner according to standard formats.