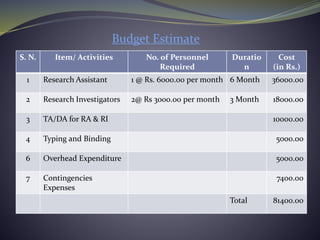
The document outlines a research project's essential components, including objectives, stakeholder analysis, and guidelines for developing a research design. It details steps from identifying a research problem and reviewing literature to data collection and report writing, including time and budget estimates for each phase. A comprehensive planning approach is emphasized to ensure successful implementation and evaluation of the research project.