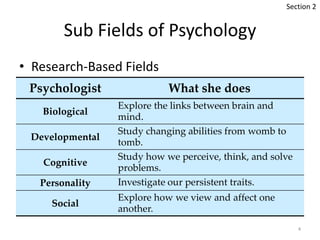
Psychology has several basic perspectives that seek to explain behavior, including biological, evolutionary, psychodynamic, behavioral, cognitive, and social-cultural perspectives. There are three main types of psychologists: basic researchers who conduct academic research, applied psychologists which make up most psychologists and include clinical psychologists, and psychiatrists who are medical doctors focused on the brain and can prescribe medication. The main subfields of psychology include biological, developmental, cognitive, personality, social, and psychometrics for research-based fields, and clinical, counseling, educational, and industrial/organizational for applied fields.