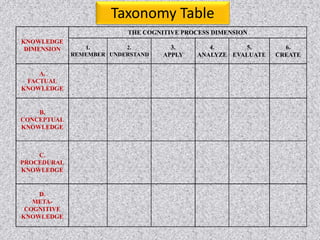
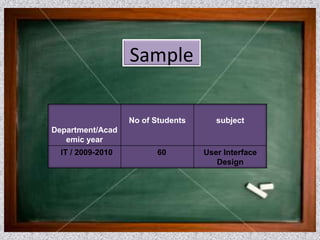
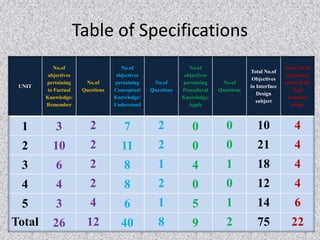
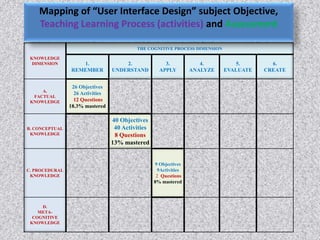
This document outlines issues related to research and class room research. It discusses identifying an appropriate research topic and guide. Finance is a major issue, including costs of experiments, materials, and attending conferences. Identifying the right research topic depends on the guide's specialization and interests of other students. The relationship between guides and students can impact research. Research scholars must develop skills like acquiring knowledge, problem solving, and being lifelong learners with self-discipline. Classroom research examines best practices for teaching-learning processes and evaluating students based on Bloom's taxonomy. Research outcomes from books discuss findings on the 10,000 hours rule for expertise and characteristics of cheating teachers.