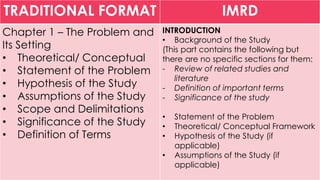
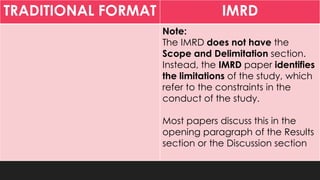
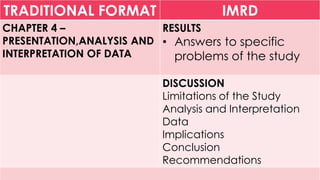
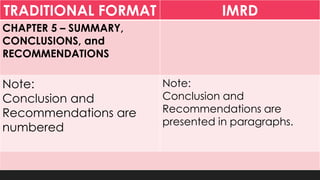
This document discusses the traditional IMRD format for research papers and theses. It describes the typical sections included in the introduction, methods, results, and discussion sections. The introduction includes the background, problem statement, framework, and research questions or hypotheses. The methods section outlines the research design, participants, data collection procedures, and analysis methods. The results section presents the key findings from the research. Finally, the discussion section analyzes and interprets the results, discusses limitations, and provides conclusions and recommendations.