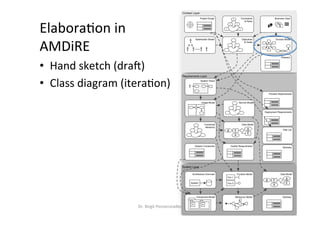
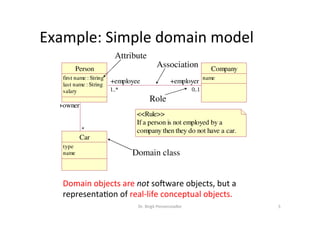
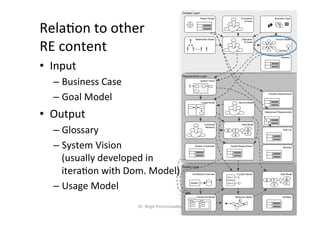
The document discusses domain models in requirements engineering. It defines a domain model as a conceptual model that describes all topics related to a specific problem domain, including entities, attributes, roles, relationships, and constraints. It provides examples of domain models for a learning network and health insurance plan. It also outlines the process for developing a domain model and discusses challenges such as ensuring completeness and understanding the problem domain.


![Example: Sample domain model for a
health insurance plan
Dr. Birgit Penzenstadler 9
[Kishorekumar, Wikimedia Commons 2009]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017springcecs-54210-domainmodels-170720091838/85/Requirements-Engineering-Domain-Models-9-320.jpg)
![Example: Sample domain model for a
health insurance plan
Dr. Birgit Penzenstadler 10
[hMp://scaledagileframework.com/domain-modeling/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017springcecs-54210-domainmodels-170720091838/85/Requirements-Engineering-Domain-Models-10-320.jpg)
![Example: Sample domain model for a
health insurance plan
Dr. Birgit Penzenstadler 11
[hMp://scaledagileframework.com/domain-modeling/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017springcecs-54210-domainmodels-170720091838/85/Requirements-Engineering-Domain-Models-11-320.jpg)

![Example: TENCompetence
learning
network
Dr. Birgit Penzenstadler 13
[hMp://dspace.ou.nl/handle/1820/649]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017springcecs-54210-domainmodels-170720091838/85/Requirements-Engineering-Domain-Models-13-320.jpg)
![Example: Research Compu?ng
Domain Model
Dr. Birgit Penzenstadler 14
[hMp://www.bridging-the-gap.com/domain-models/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017springcecs-54210-domainmodels-170720091838/85/Requirements-Engineering-Domain-Models-14-320.jpg)