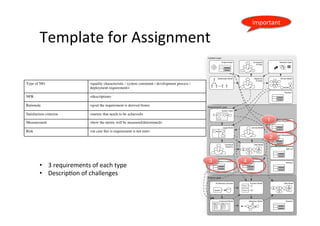
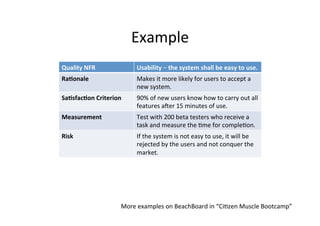
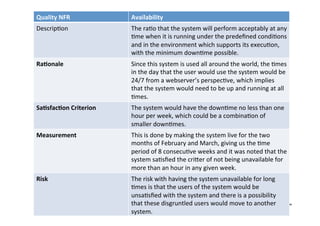
The document focuses on the classification and challenges of non-functional requirements (NFRs) in requirements engineering, emphasizing their importance for system quality and functionality. It outlines dimensions for classifying requirements, examples of quality and process requirements, and specific NFRs, such as usability, availability, and accessibility. Additionally, it discusses the challenges of elicitation, evaluation, and modeling of NFRs, highlighting their impact on system design and user satisfaction.