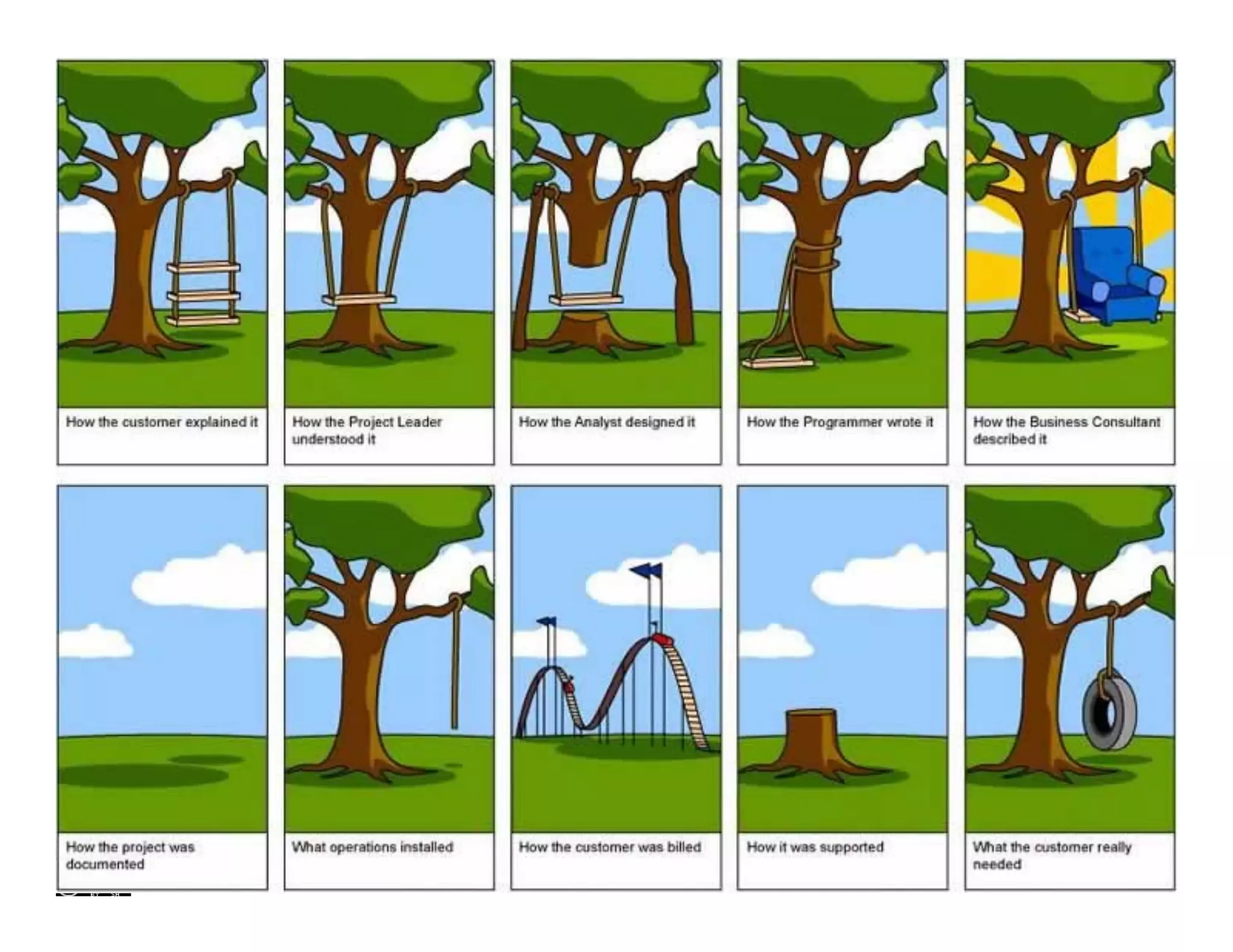
Requirements engineering (RE) is a systematic approach to articulating an explicit requirements specification agreed upon by stakeholders, incorporating phases such as elicitation, analysis, specification, and validation. Challenges in RE include incomplete requirements, communication flaws, and changing goals, which complicate successful requirements measurement. Requirements management (RM) complements RE by managing the entire software lifecycle's requirements, including documentation, change management, and traceability.








![What is a Requirement?
• Def.: A requirement is
1. a constraint/ability/characteris1c that a
stakeholder requires for a product or process in
order to solve a problem or reach a goal.
2. a constraint/ability/characteris1c that a system
has to sa1sfy in order to fulfill a contract, a
standard, a specifica1on or other given formal
documents.
3. a documented representa1on of a constraint/
ability/characteris1c as defined in 1. or 2.
Dr. Birgit Penzenstadler 19
Source: IEEE-Standard, Std. 610.12-1990 [IEEE610.12.1990]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017springcecs-5421-170719141140/75/Requirements-Engineering-Introduction-10-2048.jpg)