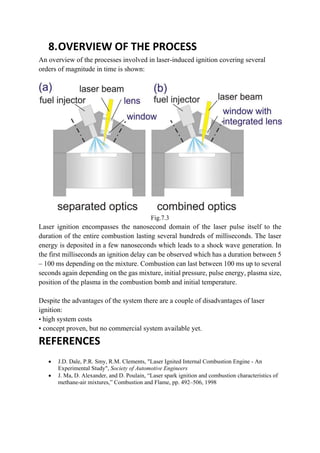
Laser ignition is an alternative ignition method for internal combustion engines that uses focused laser beams to ignite fuel-air mixtures. It has several advantages over conventional spark plug ignition, including flexible ignition location that is not constrained by plug placement. The laser ignition process begins with multiphoton ionization that releases seed electrons, which then undergo inverse bremsstrahlung absorption to rapidly increase in kinetic energy. This triggers an electron avalanche that breaks down the gas and creates a hot plasma capable of igniting the fuel. Laser ignition requires higher minimum energies than spark ignition due to energy losses along the beam path and low probability of finding seed electrons in the small focal volume. However, it offers benefits such as reduced emissions and longer lifetime.