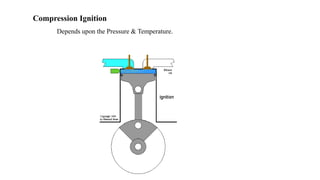
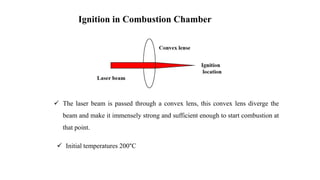
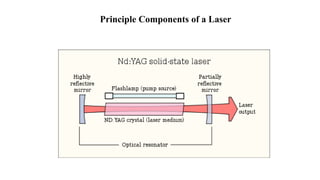
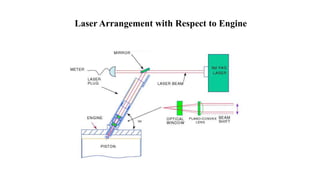
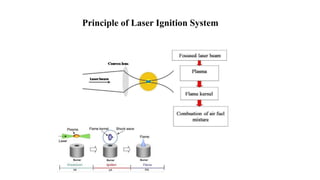
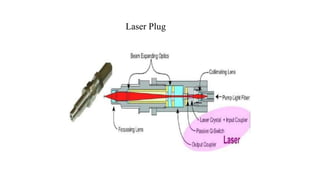
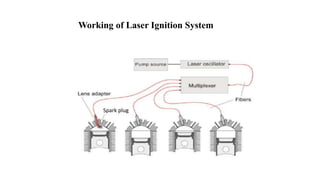
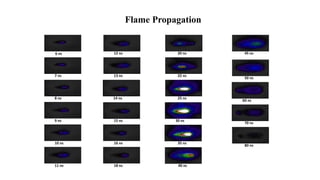
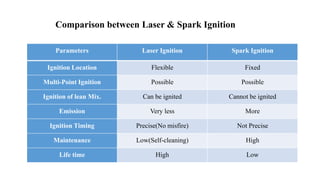
This document presents a study comparing laser ignition systems to traditional spark plug ignition systems in automotive engines. The laser ignition system offers several advantages, including complete combustion of the air-fuel mixture, lower emissions, and flexibility in ignition location, potentially revolutionizing engine performance. Despite the higher cost of laser ignition systems compared to spark plugs, their benefits may lead to broader adoption in the future.