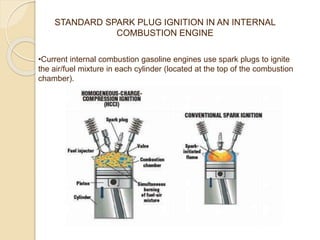
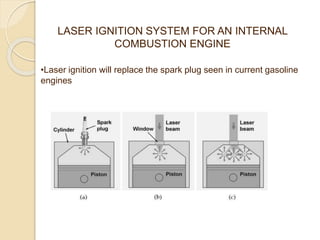
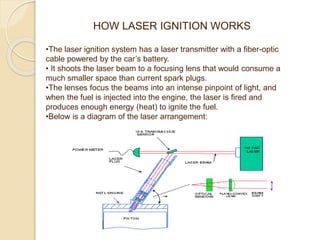
The document discusses the concept of replacing traditional spark plugs in internal combustion engines with laser ignition systems, which utilize focused laser beams to ignite the air/fuel mixture. Laser ignition offers benefits such as improved ignition efficiency, the ability to ignite leaner mixtures, and potential cost-effectiveness, as it reduces the wear on ignition components. Future research is needed to address challenges related to stability, cost, and system implementation.