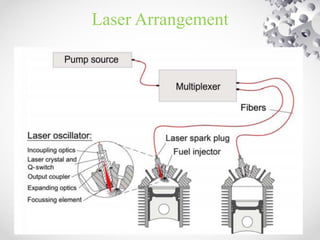
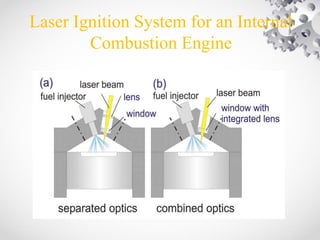
This document discusses laser ignition as an alternative to spark plug ignition in combustion engines. It begins with an introduction to laser ignition and why it may be preferable to spark plugs when igniting leaner fuel mixtures or fuels like natural gas that are more difficult to ignite. It then explains how laser ignition works by focusing a laser beam to generate a high-temperature plasma that ignites the fuel-air mixture. The document presents the experimental setup used to test laser ignition and compares it directly to spark plug ignition. It concludes that laser ignition provides advantages like improved ignition of lean mixtures and longer lifetime, though challenges around cost and optical window stability remain.