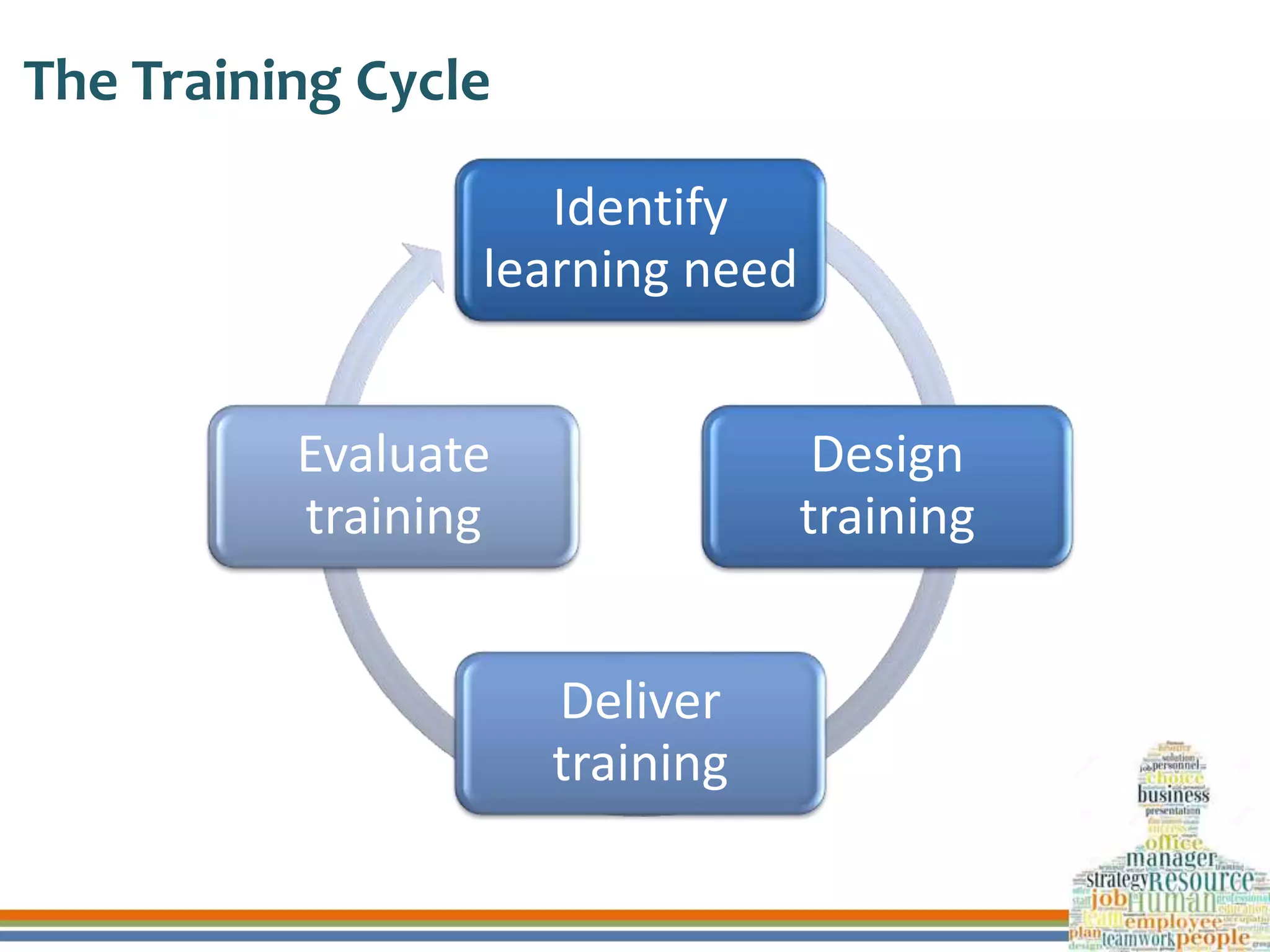
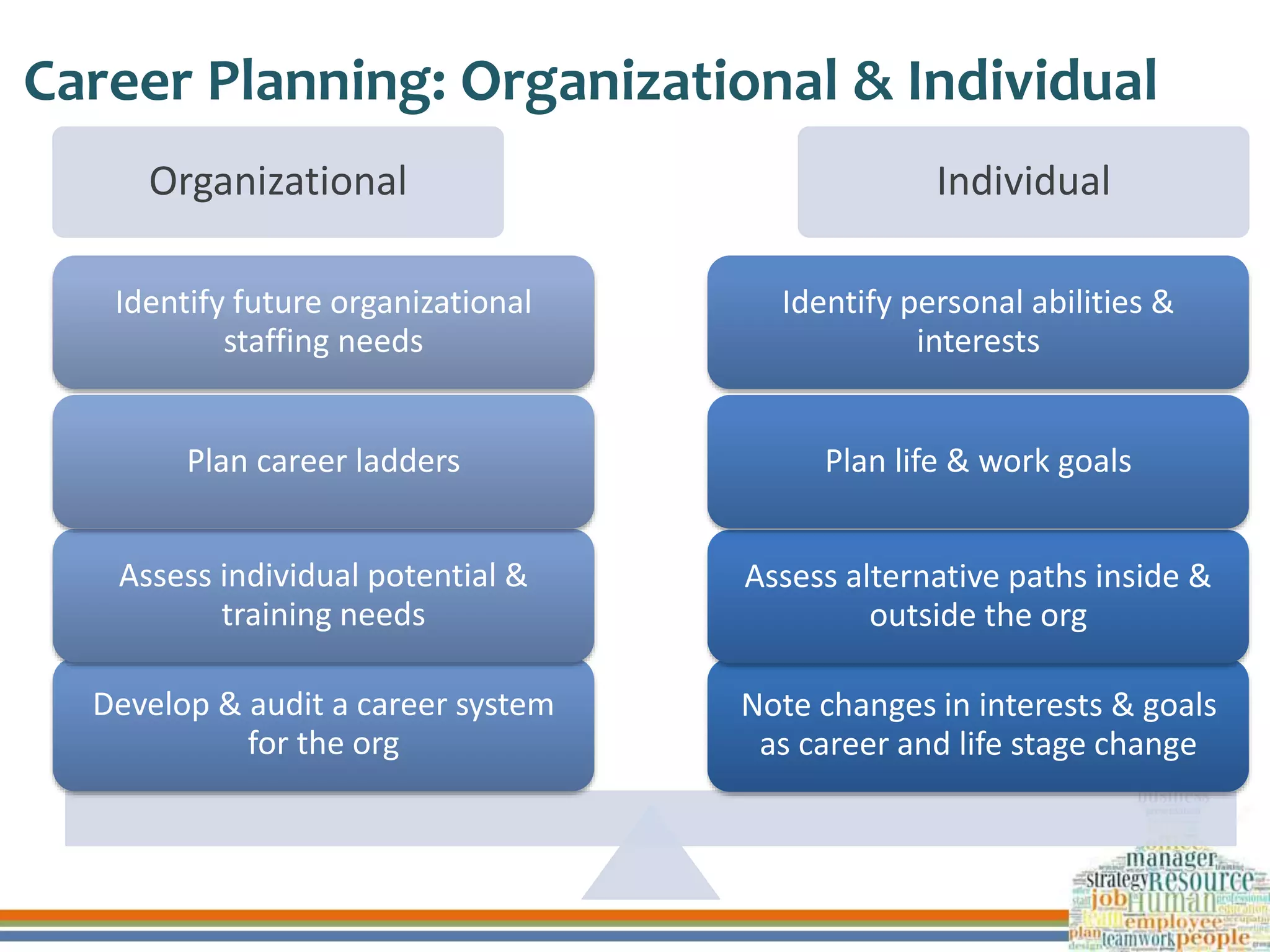
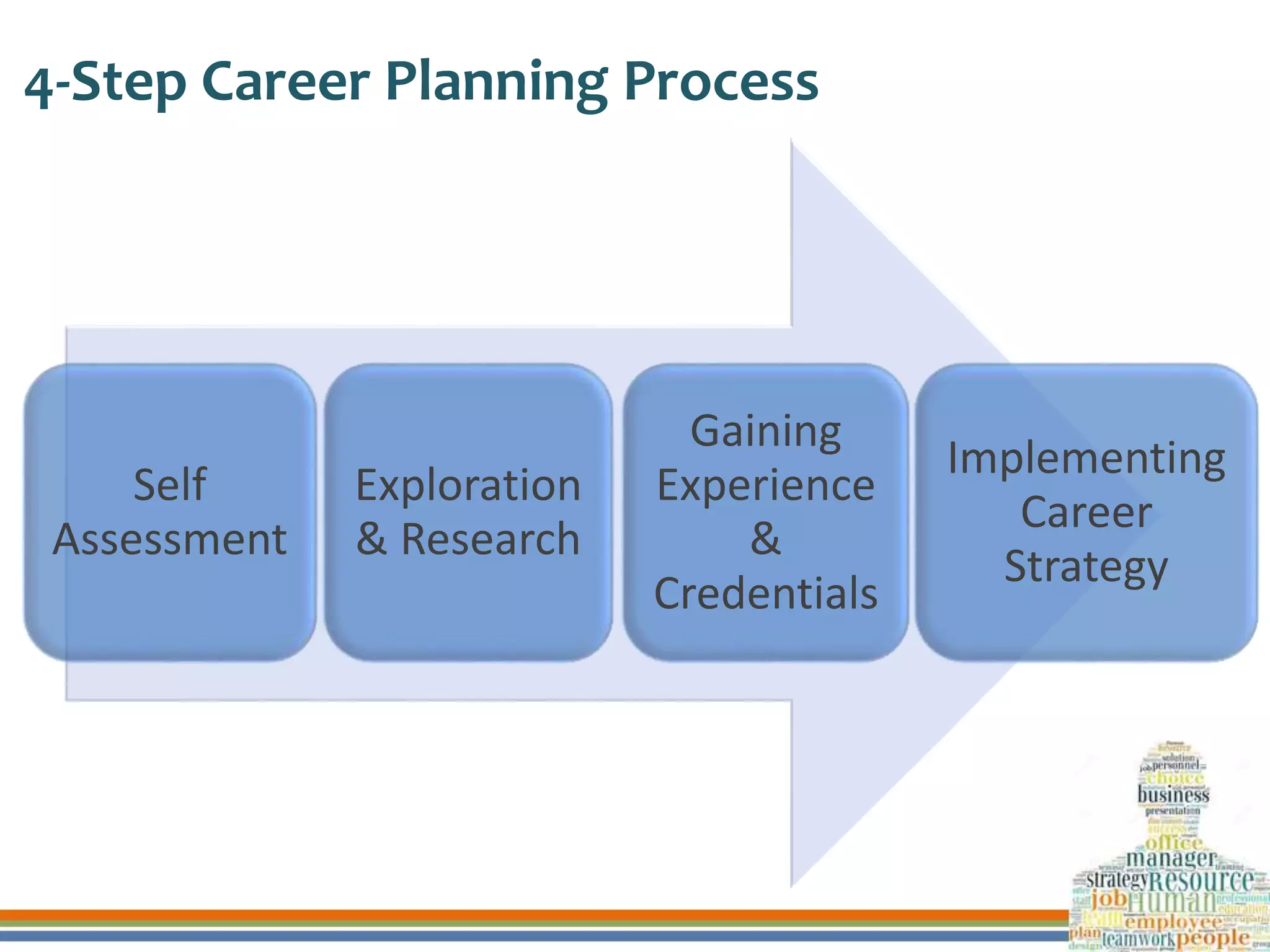
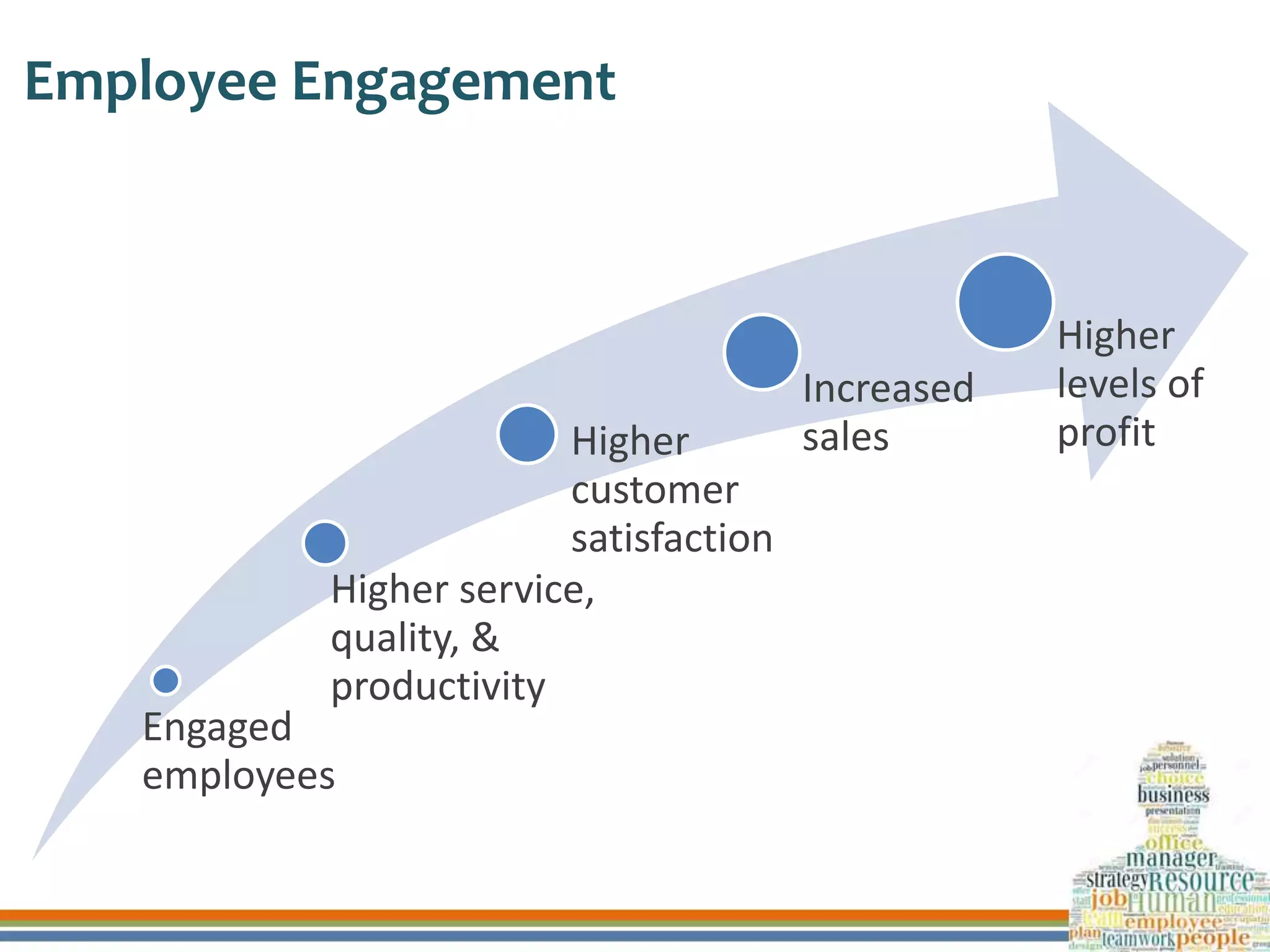
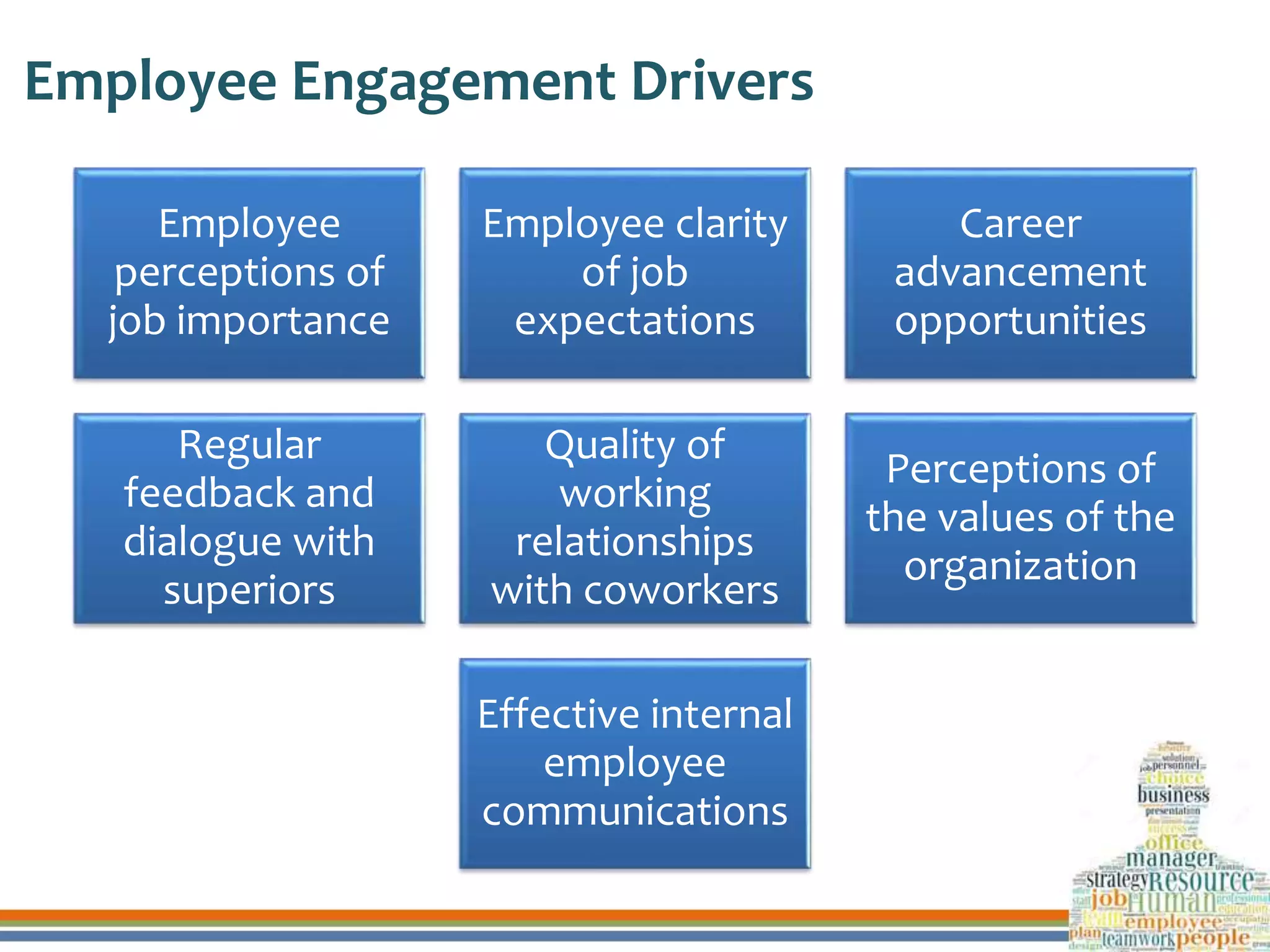
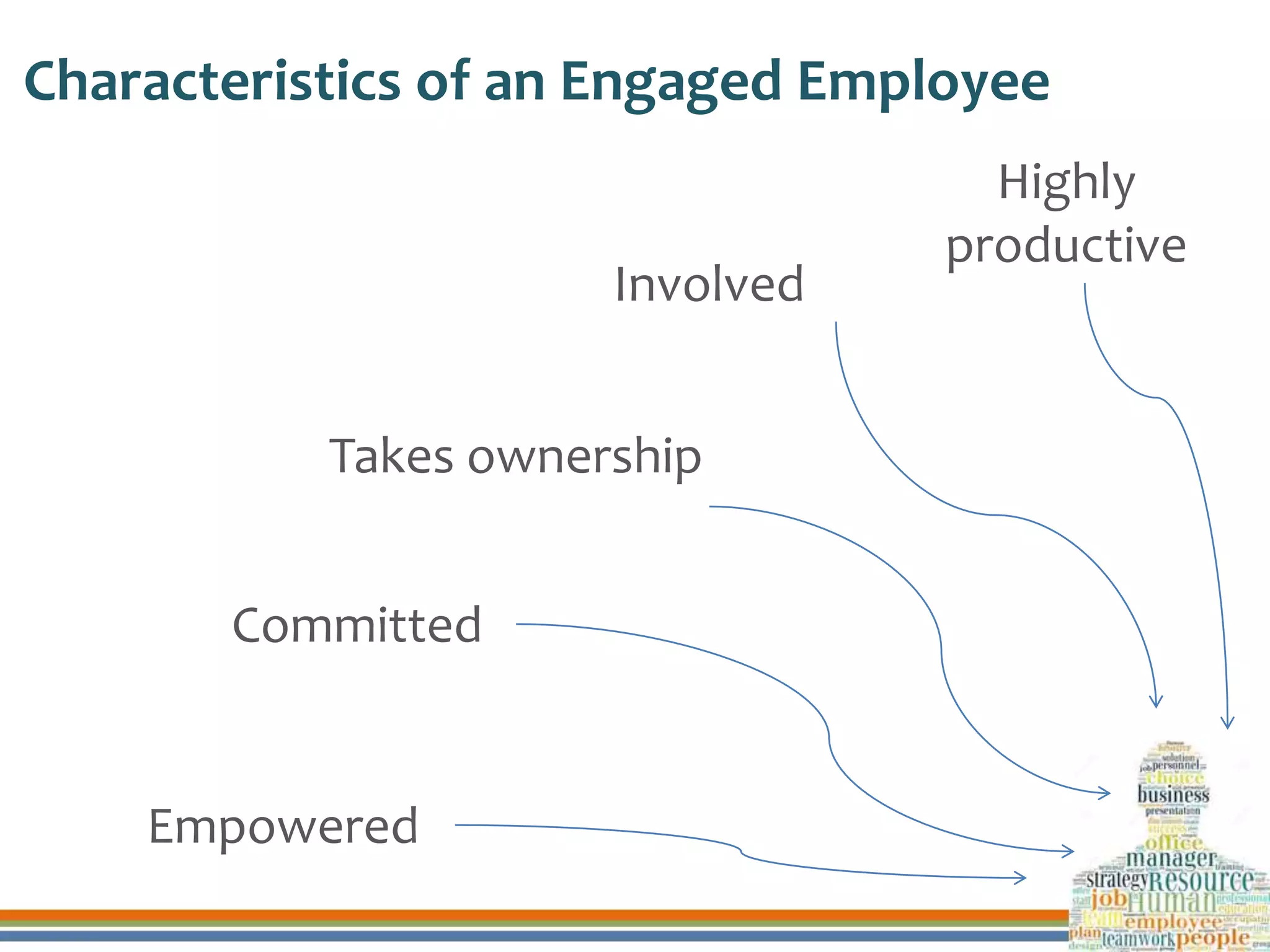
This document discusses human resource development through training, career planning, and employee engagement. It defines key terms like training, career planning, and employee engagement. It outlines the objectives and significance of training, career planning, and generating employee engagement. It also provides examples of training methods, the career planning process, and strategies to engage employees. Finally, it summarizes how three organizations ensure human resource development through these practices.