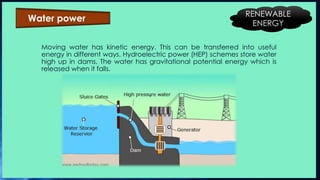
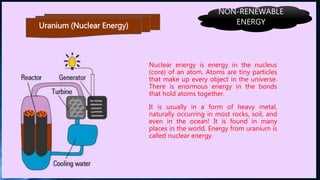
Energy exists either as renewable or non-renewable sources. Renewable sources like sunlight, wind, water and biomass will never run out. Non-renewable sources like coal, oil, gas and uranium were formed over millions of years and will deplete eventually. The document then provides details on various renewable (solar, wind, hydro, geothermal) and non-renewable (coal, oil, gas, propane, nuclear) energy sources.