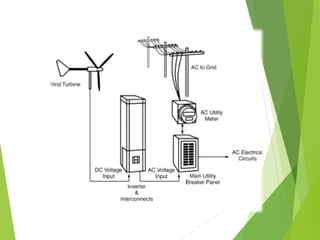
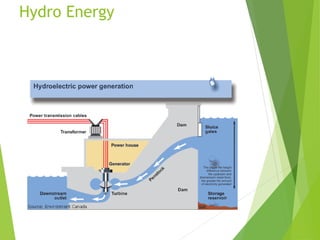
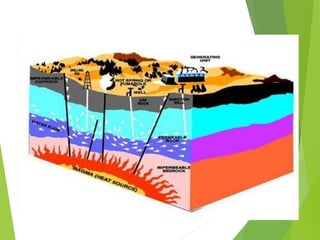
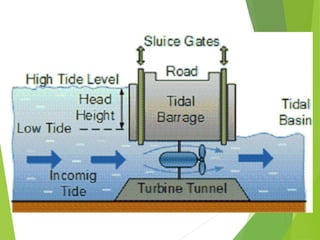
The document discusses various renewable energy resources including solar power, wind power, hydro power, geothermal energy, and tidal energy. For each energy source, it provides details on how the energy is captured and generated, as well as the pros and cons. It notes that solar remains expensive compared to other renewable sources but that technology advances have increased solar penetration. Wind power has become increasingly competitive but output is unpredictable due to weather. Hydro provides base load power but has environmental and location limitations. Geothermal and tidal energy have large-scale potential but also have specific location and cost constraints.