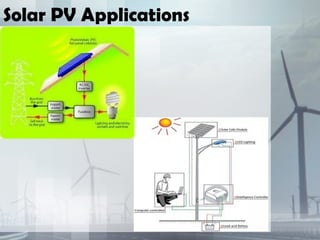
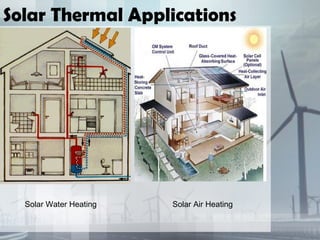
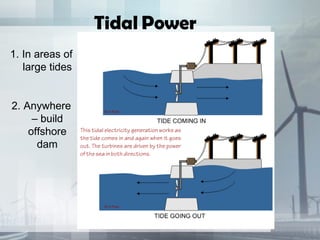
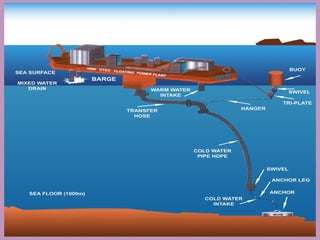
This document discusses renewable and nonrenewable resources. It defines nonrenewable resources as natural resources that cannot be replenished in a short period of time, such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas. Renewable resources are defined as those that can be replenished in a short period of time, including solar, wind, water, and biomass. For each renewable resource, the document provides a brief explanation of the resource and examples of its applications and advantages and disadvantages.