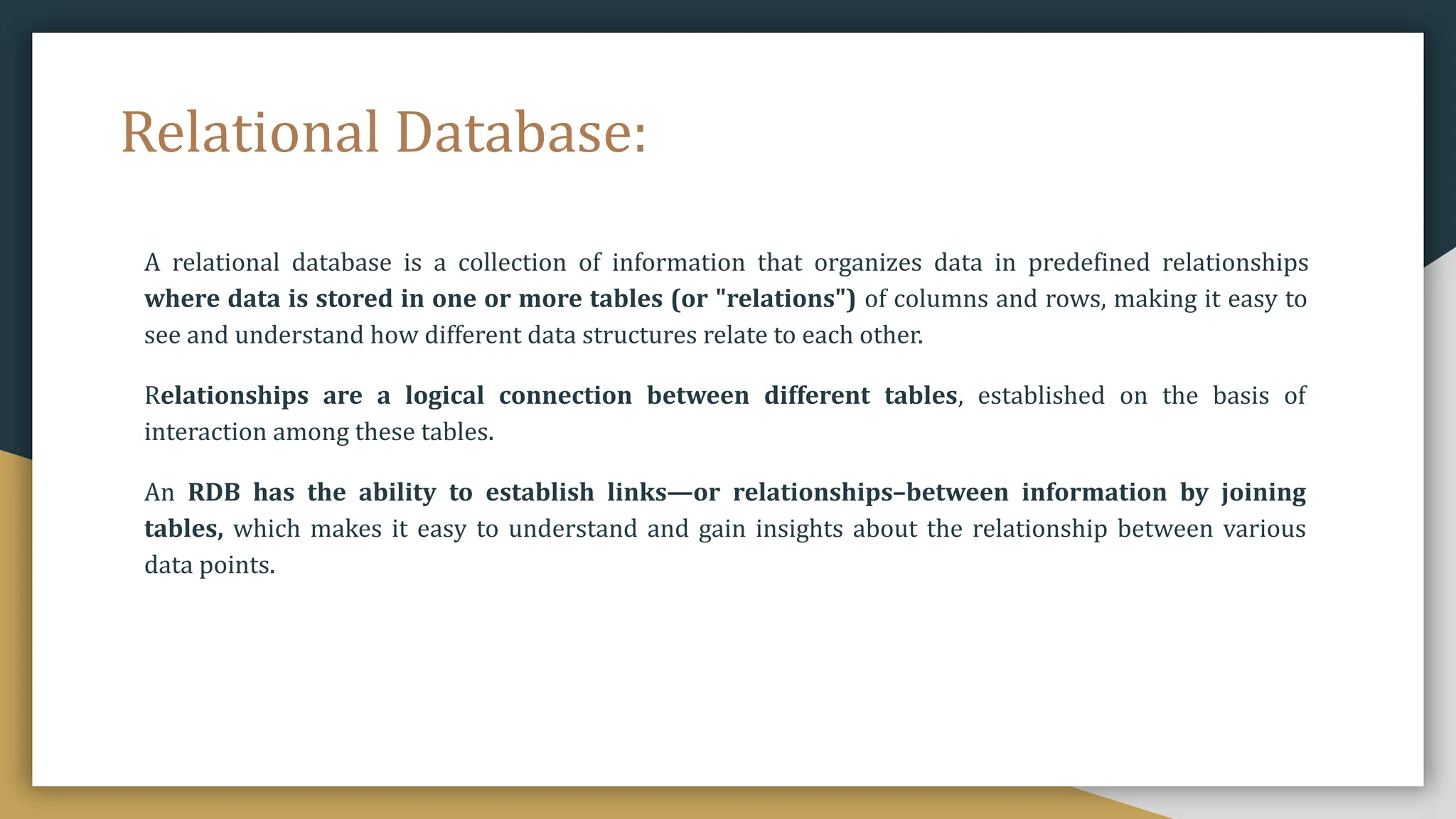
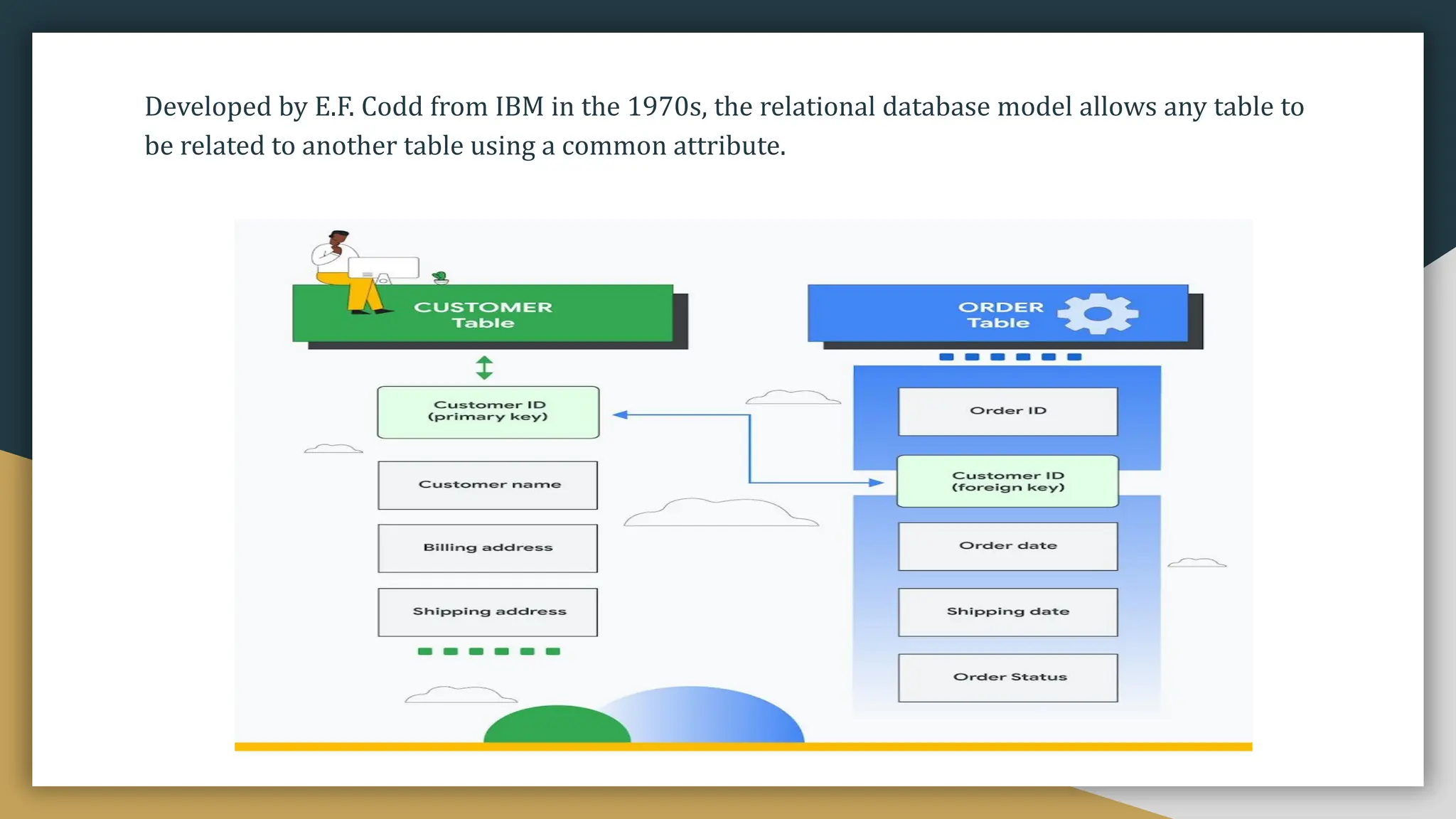
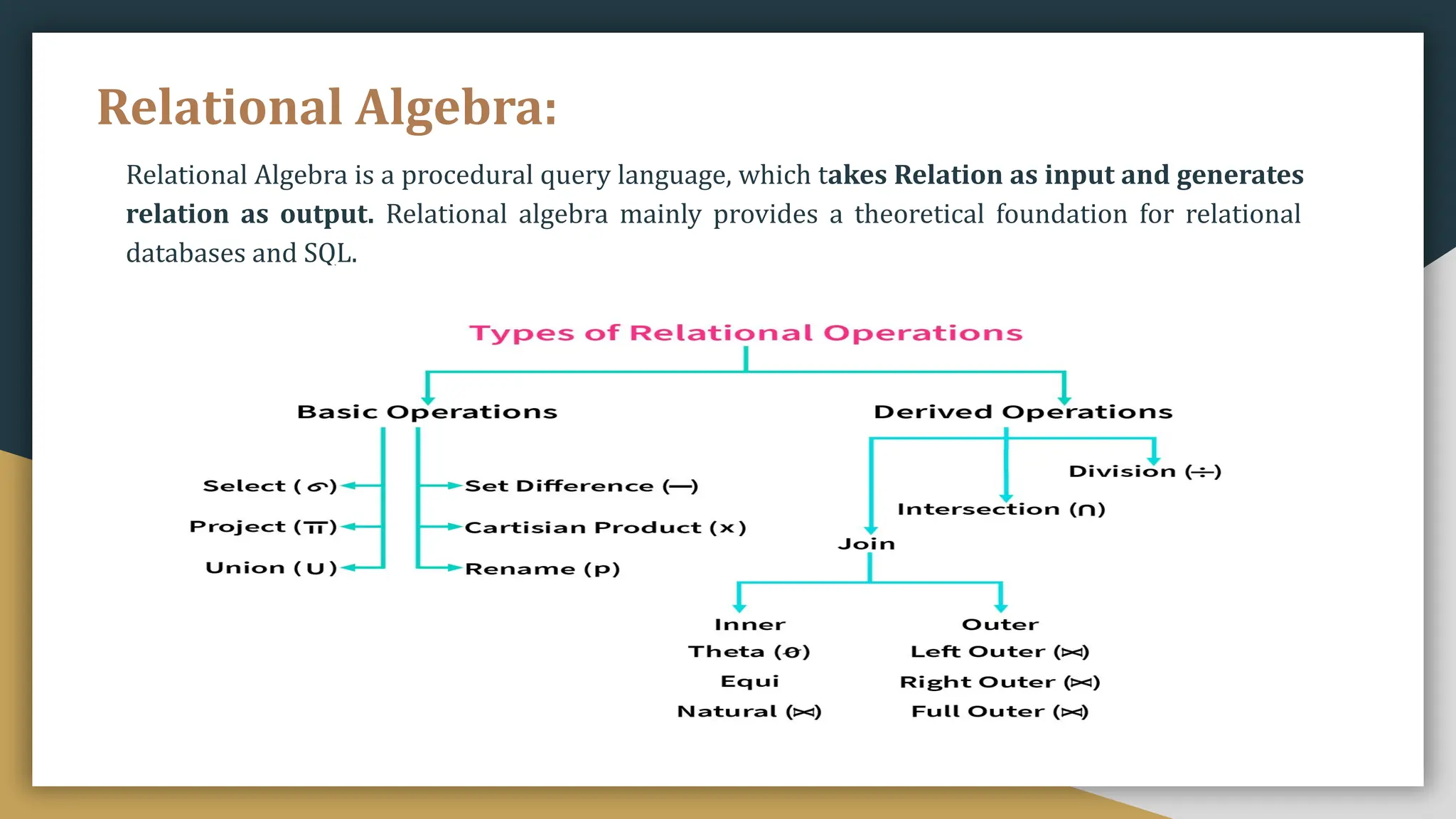
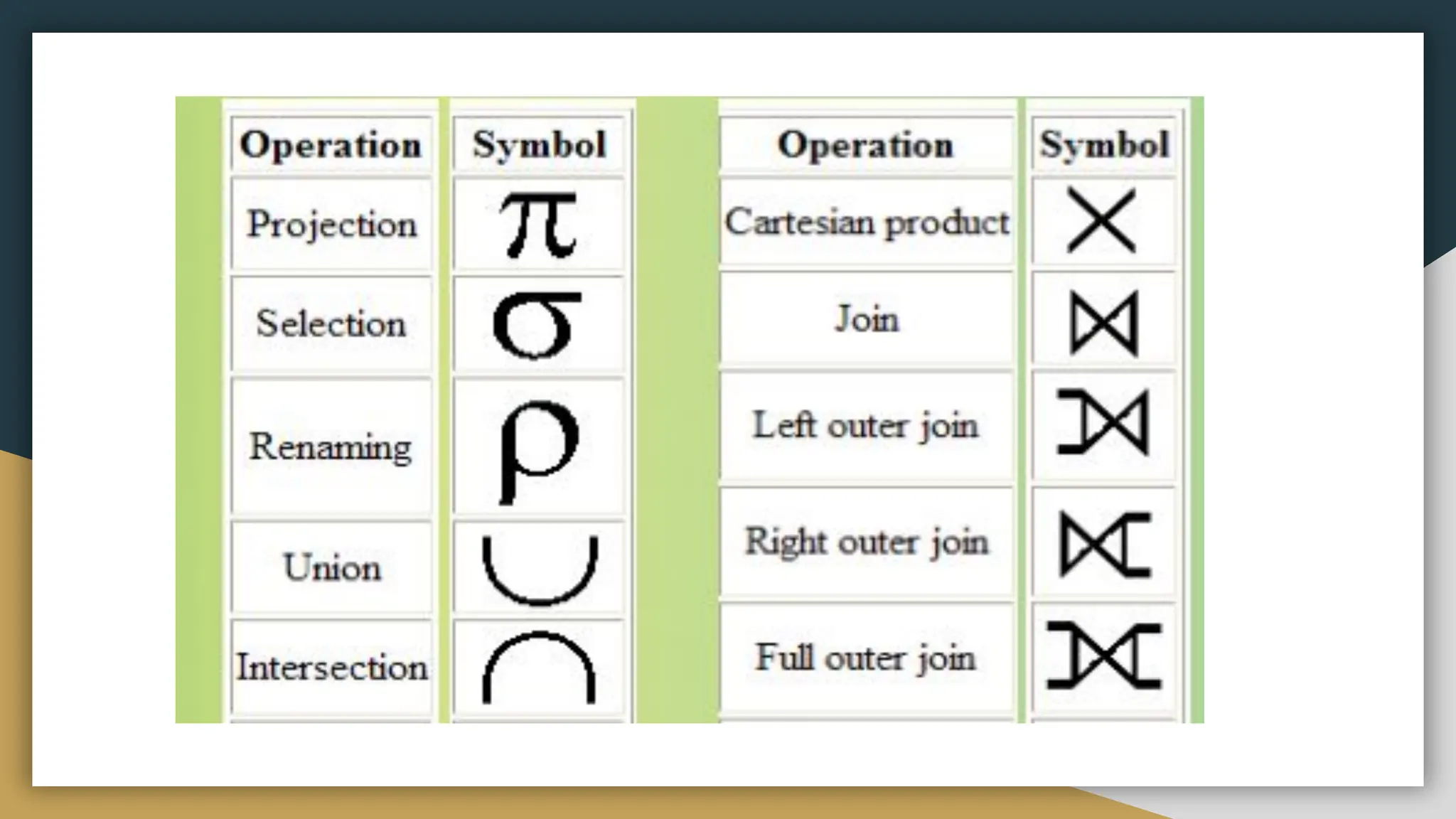
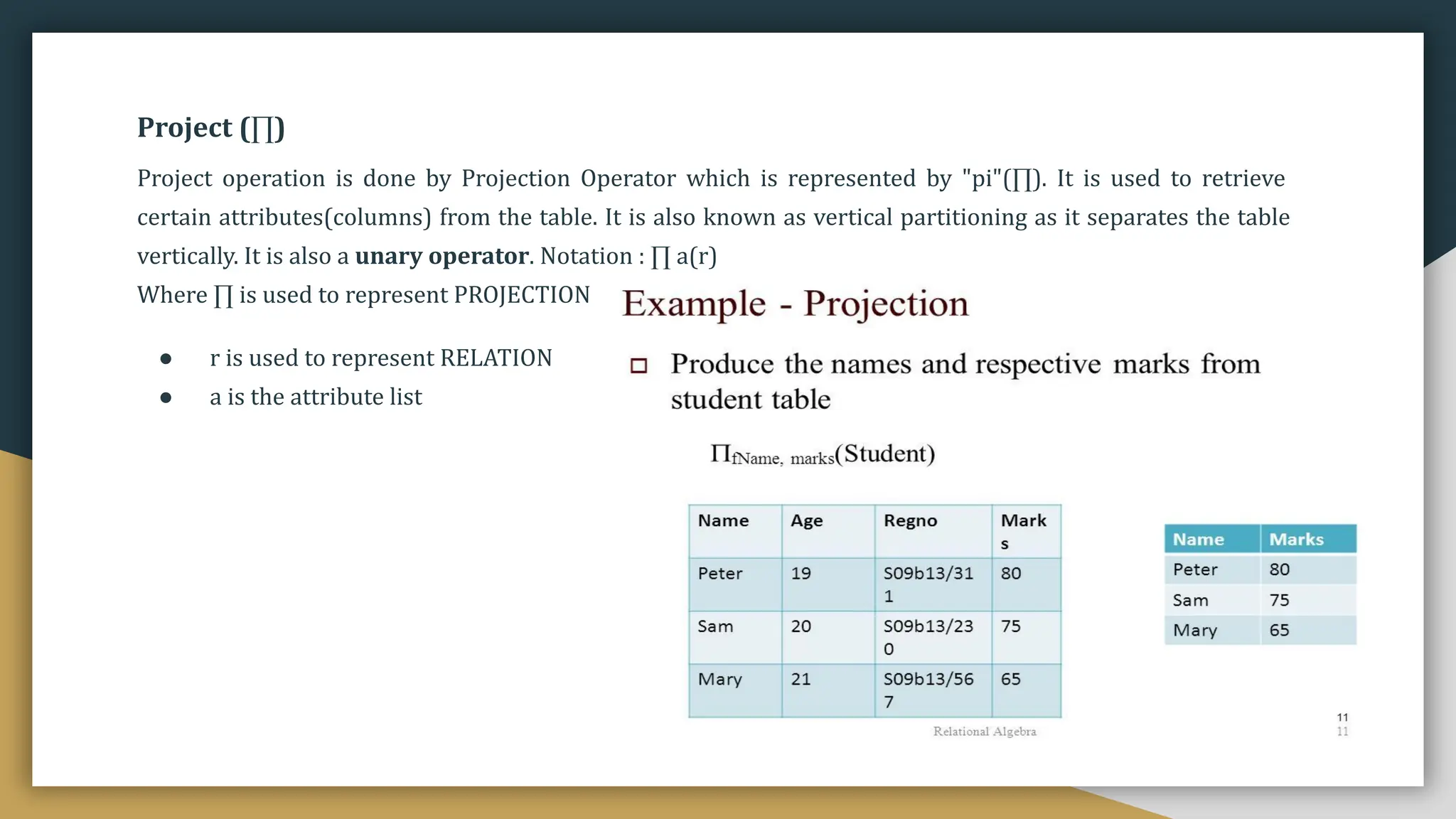
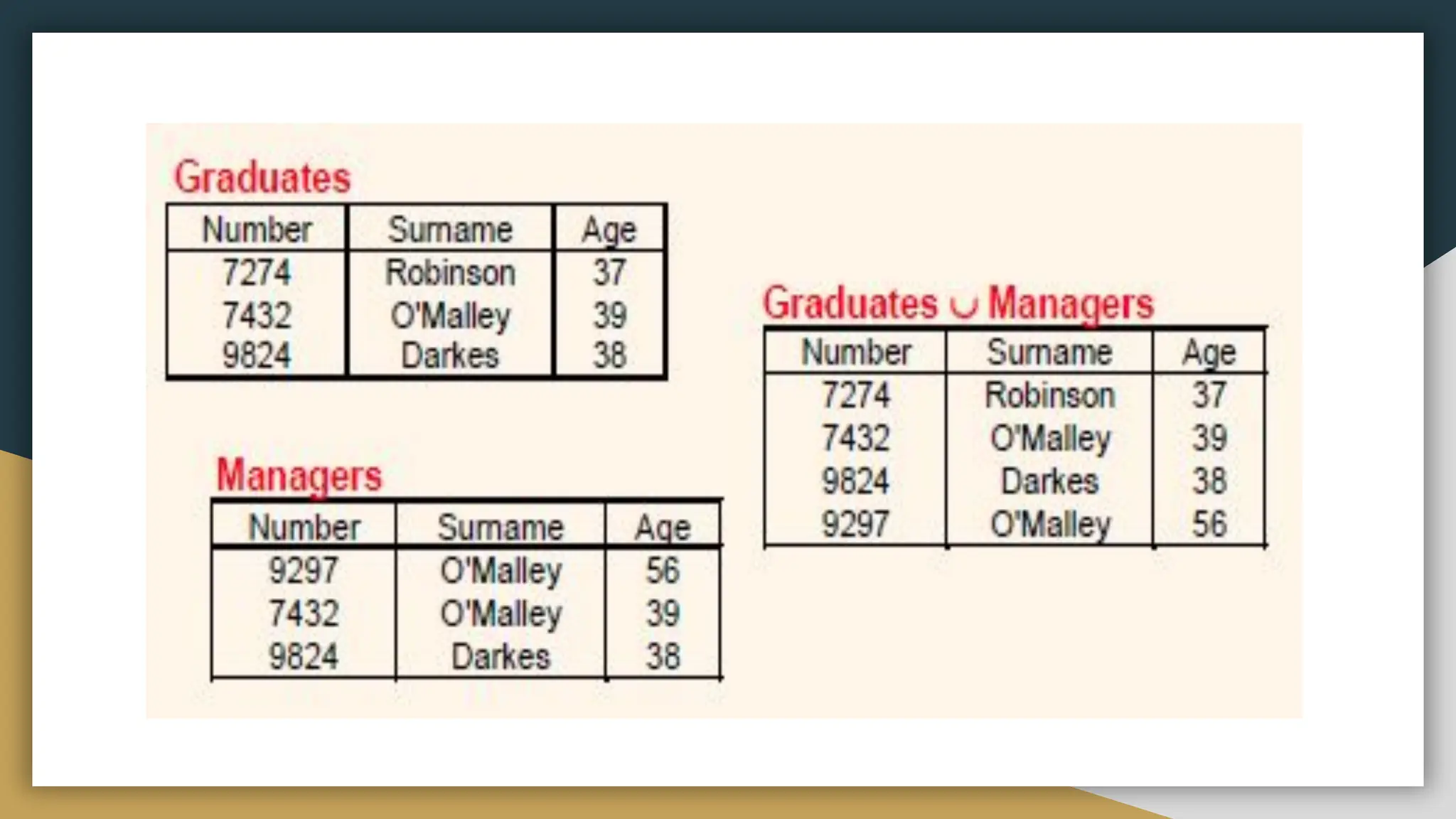
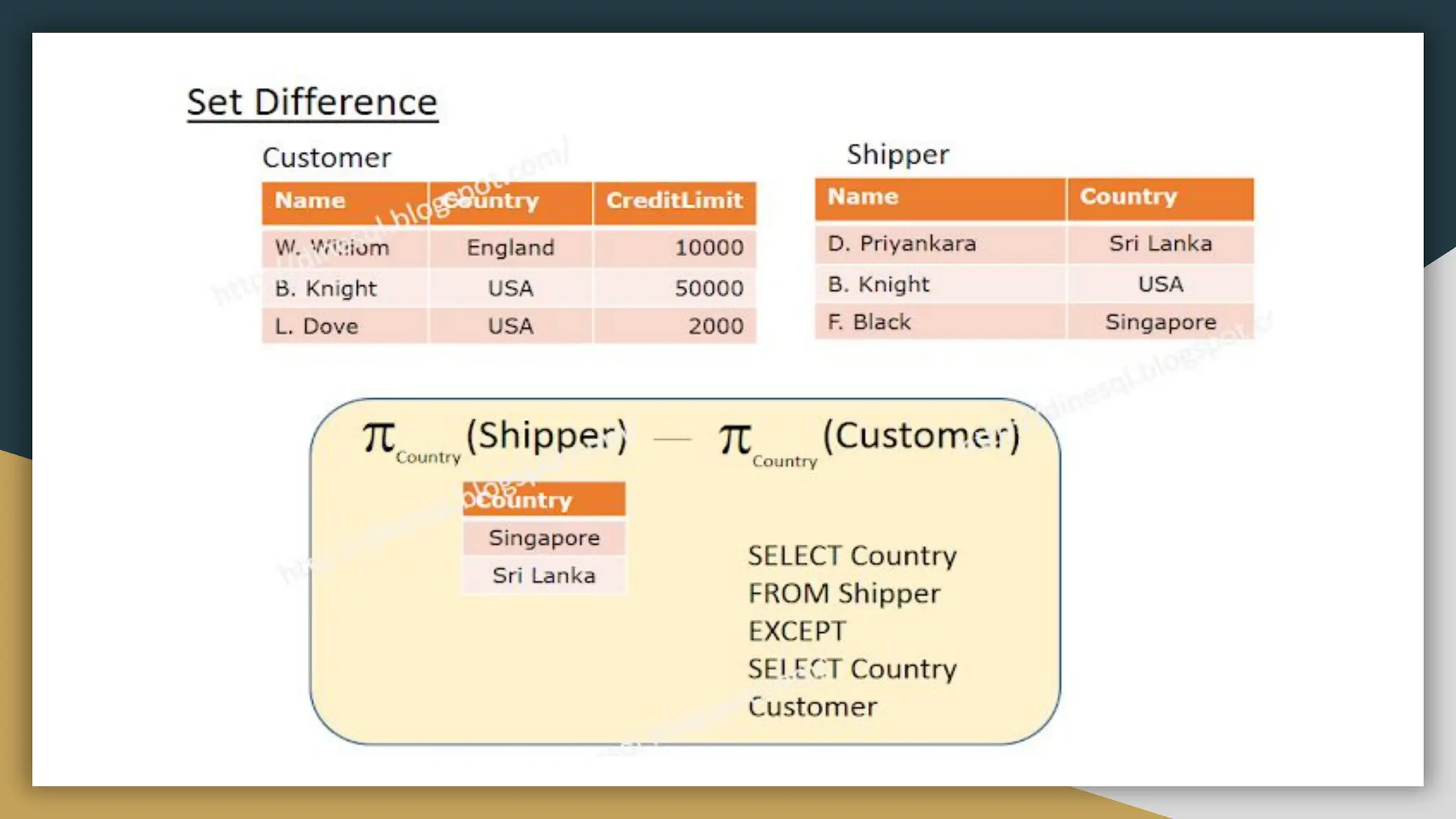
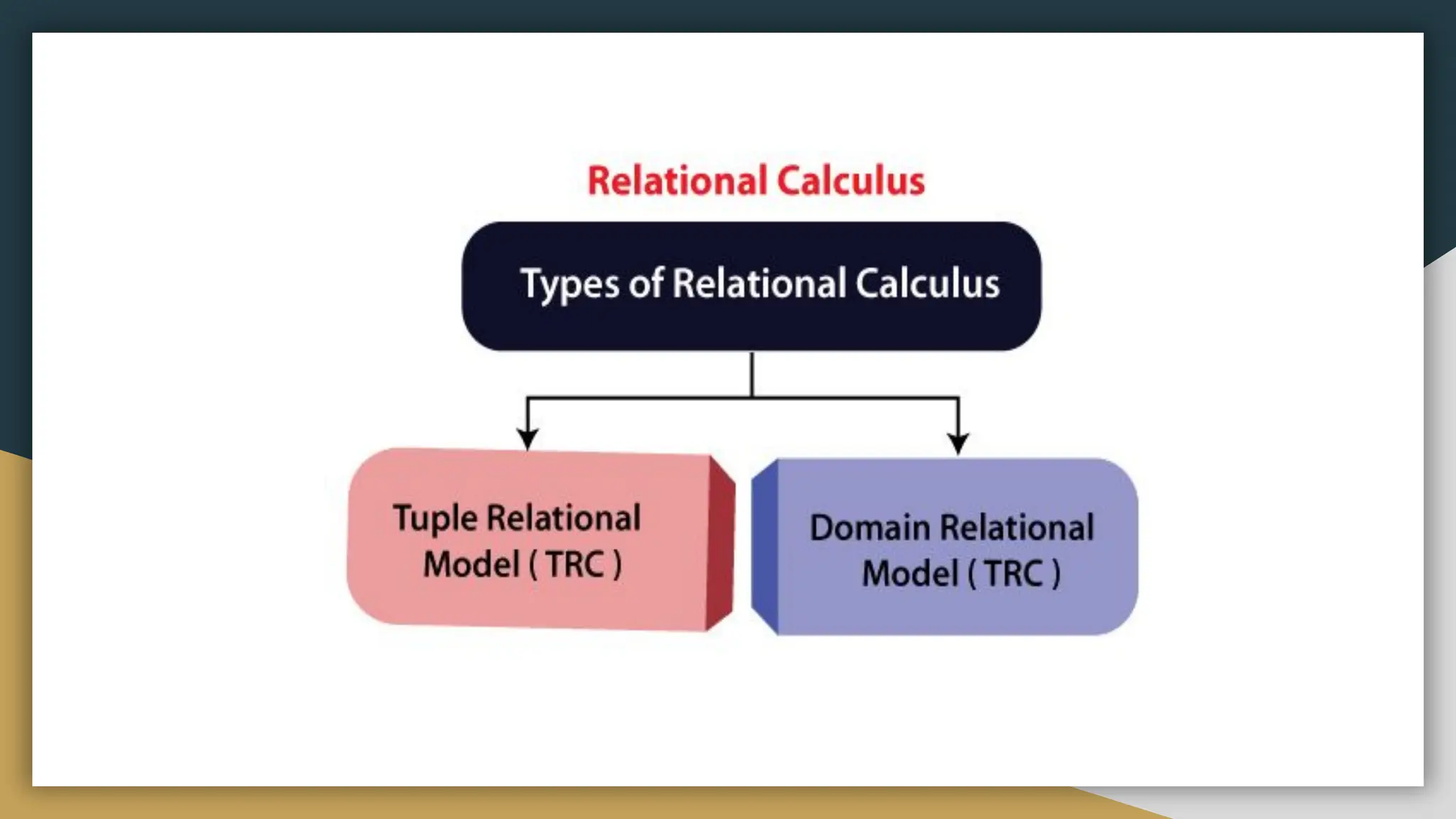
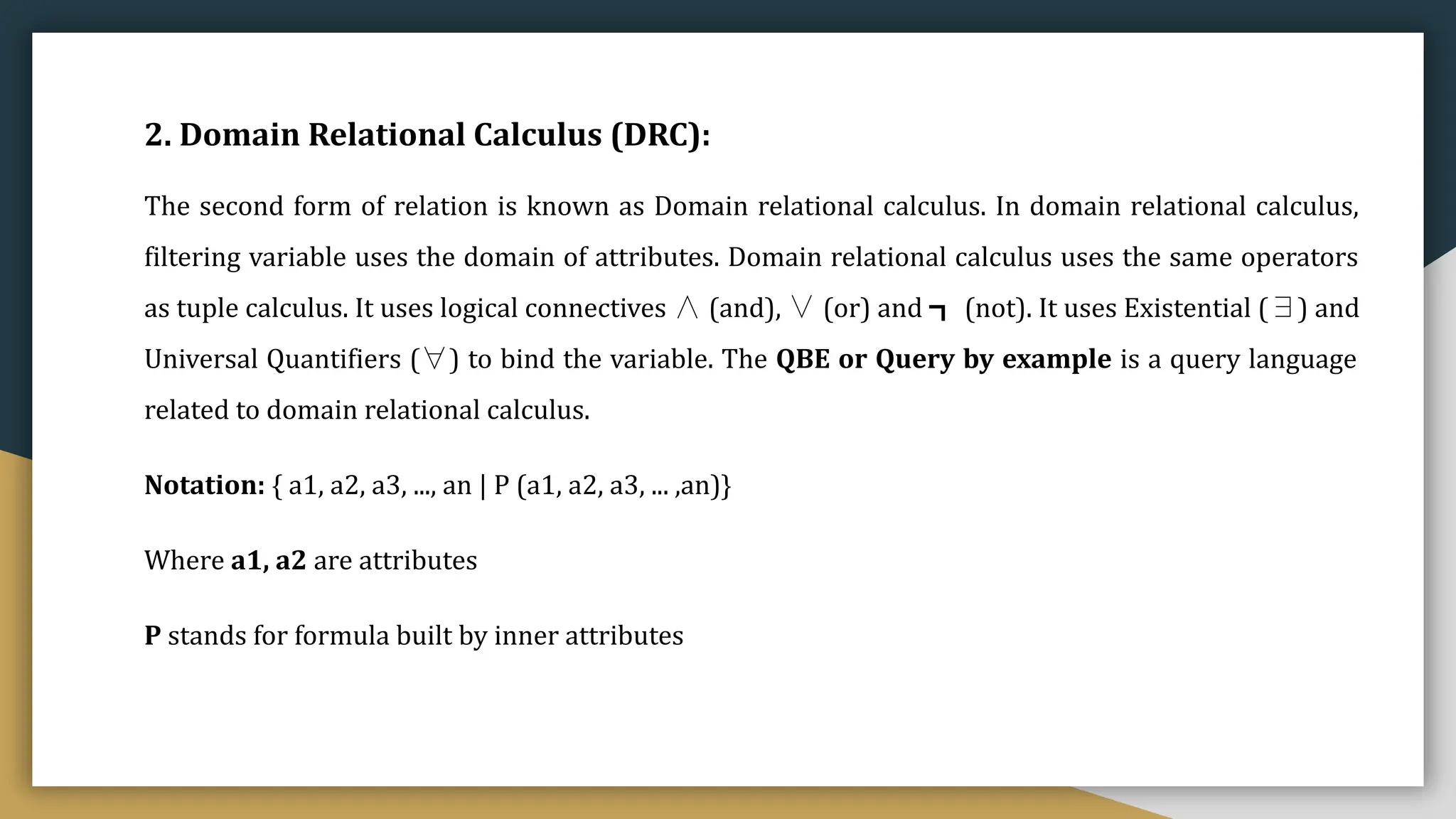
Relational databases organize data into one or more tables made up of rows and columns to show relationships between different data structures. Relationships are logical connections between tables established based on interactions among the tables. Relational algebra provides theoretical foundations for relational databases and SQL through operators like select, project, join, and union that take relations as input and output new relations. Relational calculus is a non-procedural query language that uses predicates and quantifiers to specify what to retrieve from relations rather than how to retrieve it.











![DIVISION Operation:(/)
The Divition Operation is defined on two relation r(U1) and s(U2) where U2 is the subset of U1 and s is not an
empty relation:
r÷s={t∣t∈r(U1−U2)∧satisfy}
Where satisfy=∀ts∈s(∃tr∈r(tr[U2]=ts∧tr[U1−U2]=t))
This means that for a tuple t to appear in the result of Division, the values in t must appear in r in combination
with every tuple in s.
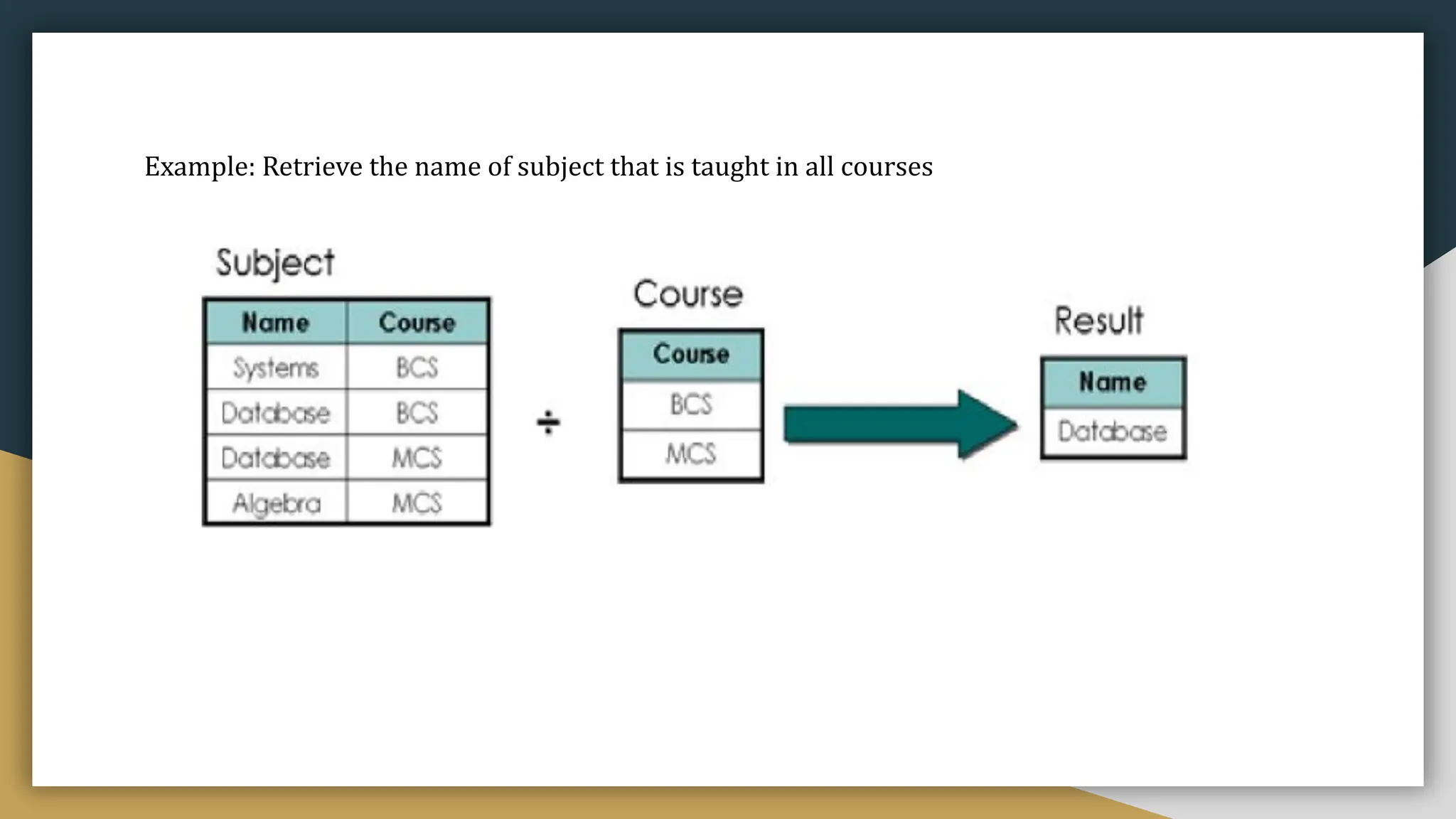
The Division is very useful for a special kind of query such as “ Retrieve the name of the student who
enrolls in all course teach by Professor Ba”
● Producing the result of the Division operation
○ Consider each subset of tuple in r that match on t[U1 – U2]
○ For this subset of tuples, take the values t[U2] from each. If this covers all tuples in s then add
t[U1 – U2]in the result.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-iidbms-240328034148-def3acf8/75/Unit-II-DBMS-presentation-for-students-pdf-30-2048.jpg)



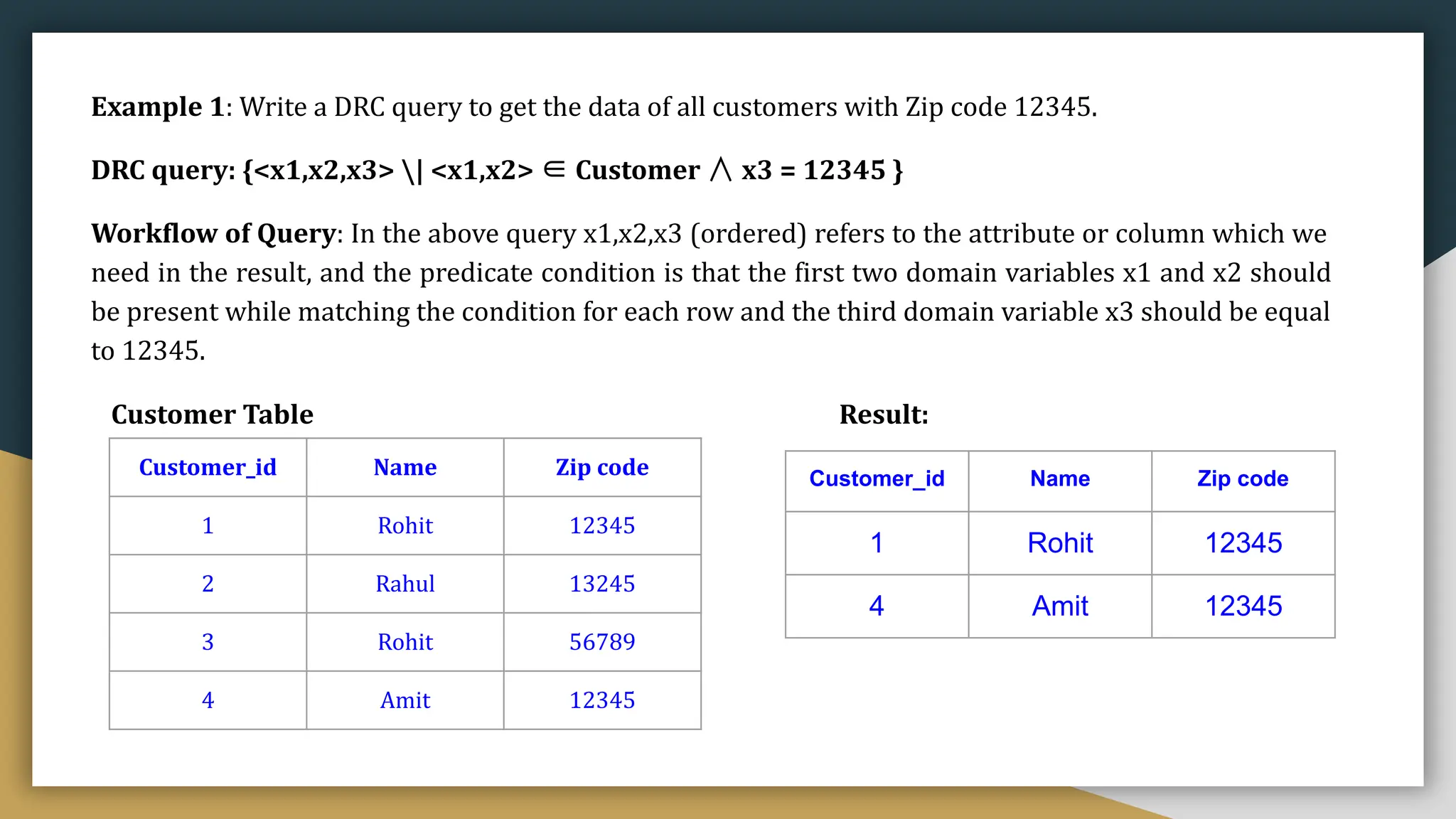
![Customer_id Name Zip code
1 Rohit 12345
2 Rahul 13245
3 Rohit 56789
4 Amit 12345.
Customer Table
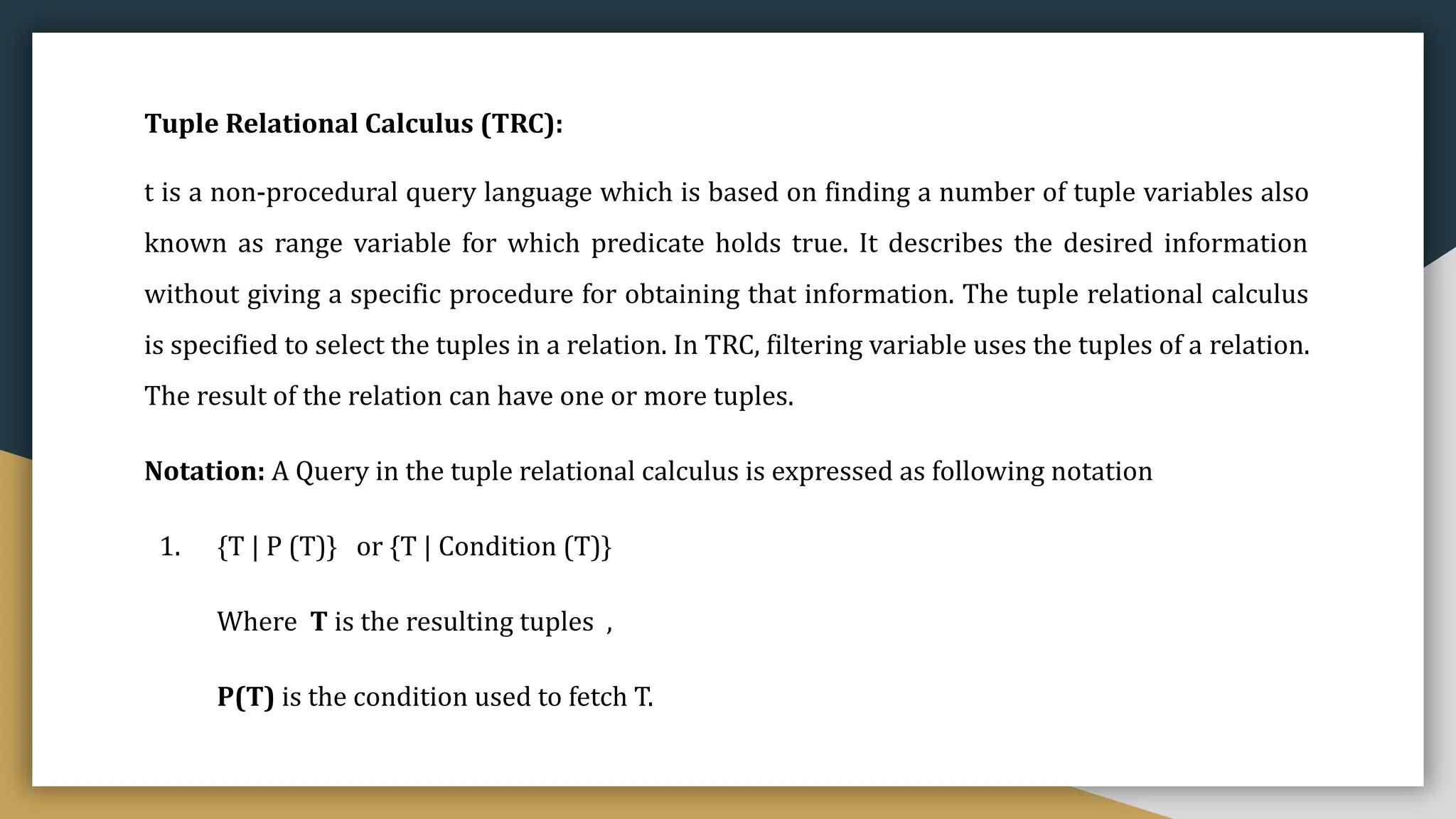
Example 1: Write a TRC query to get all the data of customers whose zip code is 12345.
TRC Query: {t | t ∈ Customer ∧ t.Zipcode = 12345} or TRC Query: {t | Customer(t) ∧ t[Zipcode] = 12345 }
Workflow of query - The tuple variable "t" will go through every tuple of the Customer table. Each row will check
whether the Cust_Zipcode is 12345 or not and only return those rows that satisfies the Predicate expression
condition.
The TRC expression above can be read as "Return all the tuple which belongs to the Customer Table and whose
Zipcode is equal to 12345."
Customer_id Name Zip code
1 Rohit 12345
4. Amit 12345
RESULT OF THE QUERY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-iidbms-240328034148-def3acf8/75/Unit-II-DBMS-presentation-for-students-pdf-37-2048.jpg)



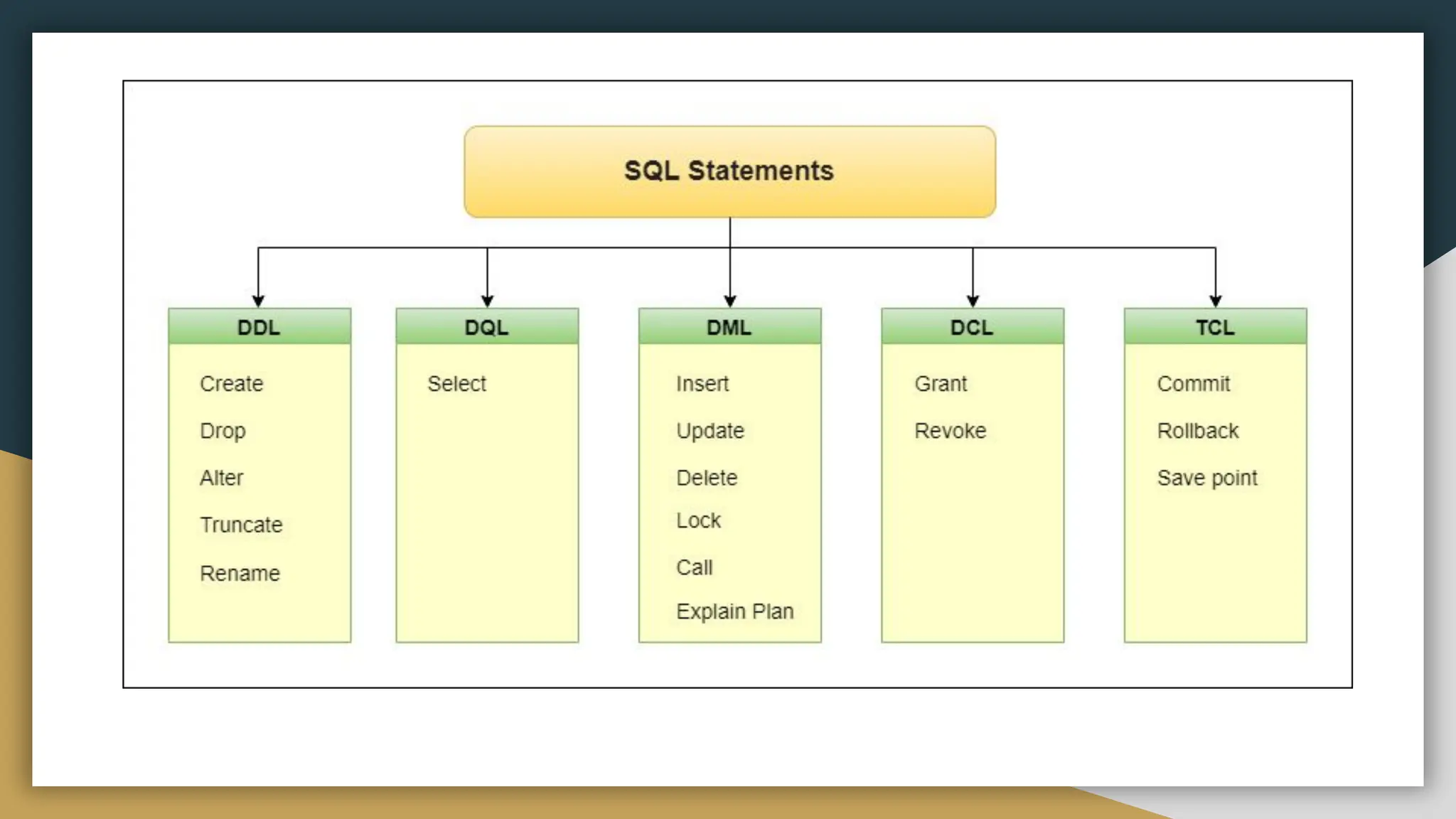

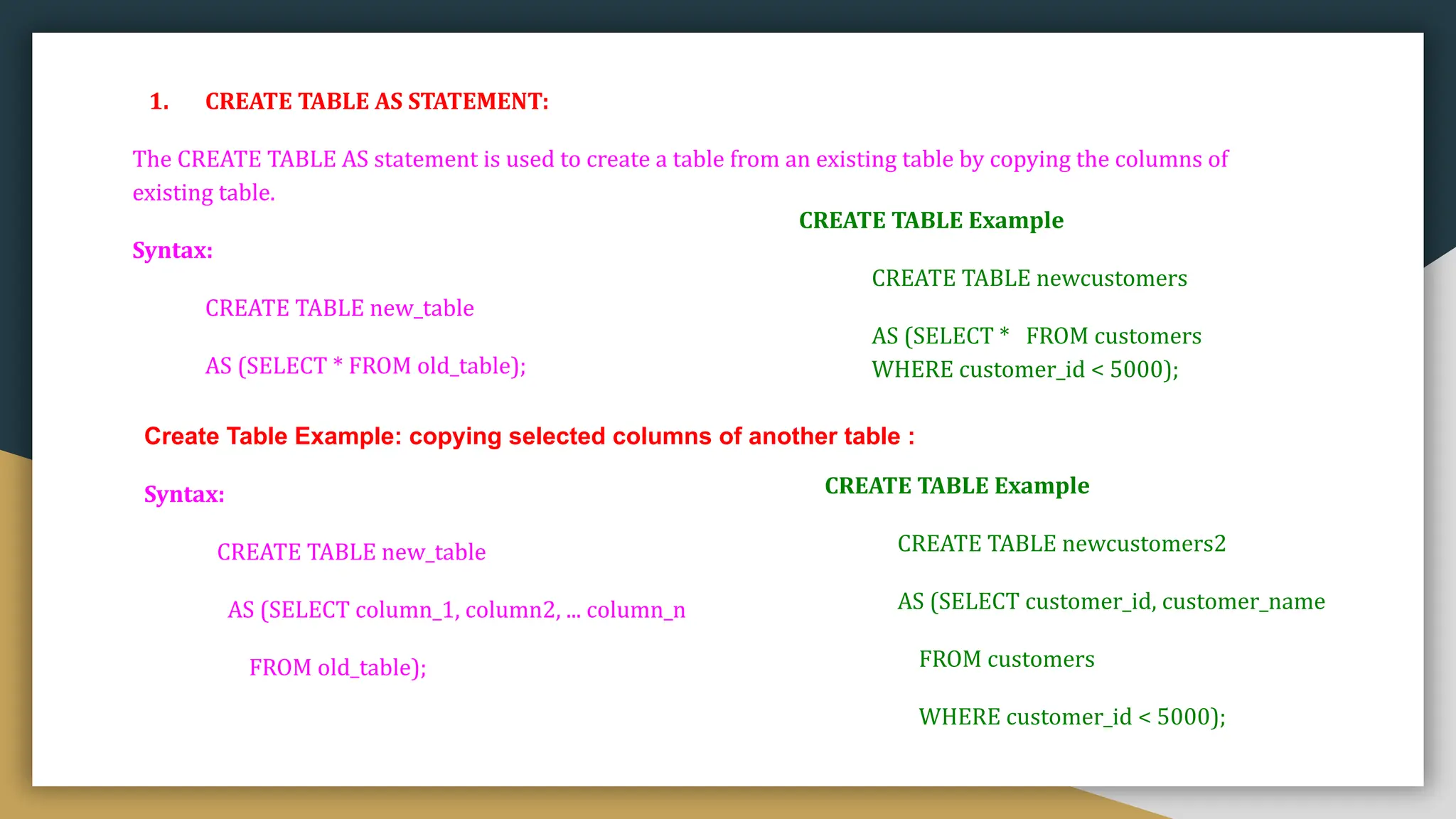
![1. CREATE TABLE:
In Oracle, CREATE TABLE statement is used to create a new table in the database.
To create a table, you have to name that table and define its columns and datatype for each column.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE table_name
( column1 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
column2 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
...
column_n datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ]
);
CREATE TABLE Example
CREATE TABLE customers
( customer_id number(10) NOT NULL,
customer_name varchar2(50) NOT
NULL,
city varchar2(50)
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-iidbms-240328034148-def3acf8/75/Unit-II-DBMS-presentation-for-students-pdf-45-2048.jpg)