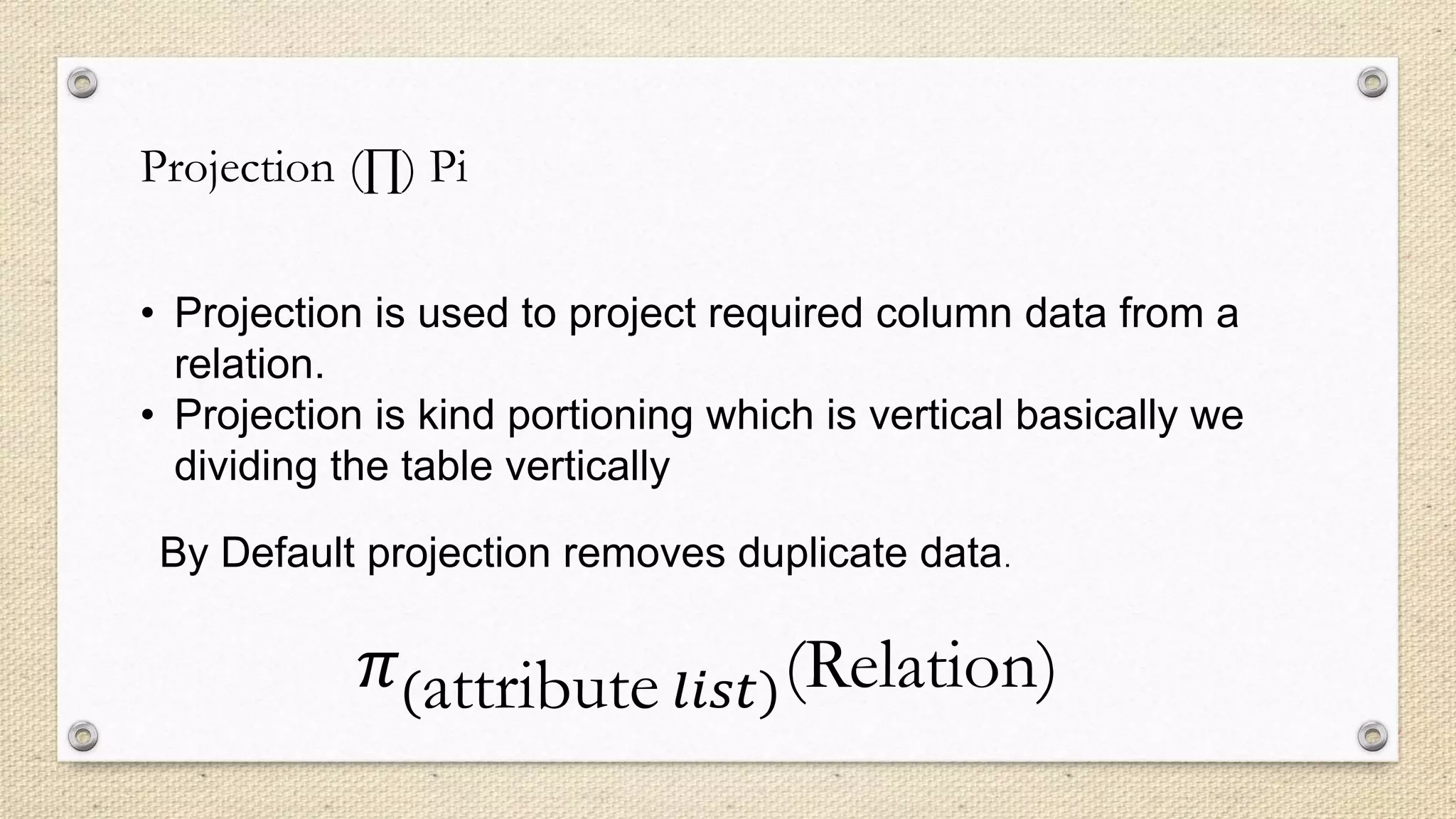
The document discusses various relational algebra operations including selection, projection, set operations, cartesian product, and rename. Selection allows retrieving data from a relation based on conditions. Projection retrieves a subset of attributes. Set operations like union and difference are used to combine relations. Cartesian product generates all possible combinations between tuples of two relations. Rename renames the output relation of an operation.









![If we will write:
σ
sal>2k[σCITY=DELHI]EMPLOYEE]
RESULT:-
3
DELHI
C 3K](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationaloperationfinal-180918171842/75/Relational-operation-final-10-2048.jpg)
![If we will write like this:
[ σ sal>2kEMPLOYEE]
RESULT:-
3 DELHI C 3K
4 CHENN
AI
D 4K
Then we will write:-
σ CITY=DELHI[σSal>2K
(EMPLOYEE)]
RESULT:-
3
DEL
HI
C 3K](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/relationaloperationfinal-180918171842/75/Relational-operation-final-11-2048.jpg)