This document discusses regulatory affairs documentation including Master Formula Records (MFRs) and Drug Master Files (DMFs). It explains that MFRs provide complete product descriptions to ensure batch-to-batch uniformity, while DMFs confidentially provide manufacturing and quality control information to regulatory agencies. Key elements of these documents are outlined, such as their structure, components, procedures for preparation and maintenance, and importance in obtaining marketing authorization and maintaining compliance.
![REGULATORY AFFAIRS
Prepared by;
Kusuma Latha Beera,
M.Pharmacy ,1st sem
GITAM Institute Of Pharmacy,
GITAM [ Deemed to be university ]
Master Formula Record (MFR)
Drug Master File (DMF)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulatoryaffairs-181118095428/75/Regulatory-affairs-1-2048.jpg)









![ Role of Master Formula Record [MFR] according to the
guidelines from different countries;
• European Guidelines : MFR is not only for every batch
but it includes manufacturing formula and
instructions to be maintained for each product that to
be manufactured in one document.
• Canadian Guidelines : MFR is set of documents
specifying the raw materials with quantities and
packaging materials with detailed descriptions of
manufacturing procedures and precautions required
to produce the specified quantity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulatoryaffairs-181118095428/85/Regulatory-affairs-11-320.jpg)






![Procedure :
A Master Formula Record is either prepared based upon
experience of competent qualified staff [ Analytical Chemist /
Manufacturing Chemist ] or prepared based upon on the
manufacturing record of a batch size.
Master Formula Record cannot be ignored. Once it is prepared
it is transferred to previous staff to new staff.
It is followed as a standard document for processing a batch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulatoryaffairs-181118095428/85/Regulatory-affairs-18-320.jpg)


![Drug Master File :
It is a document prepared by Pharmaceutical Manufacturer and
submitted solely at its discretion to appropriate regulatory
authority in the intended drug market. [ followed by submission
of information to FDA ]
It provides the regulatory authority with ;
Confidential detailed information [ Chemistry, Manufacturing &
Control
Process or articles used in manufacturing
Complete information of API or Finished dosage form](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulatoryaffairs-181118095428/85/Regulatory-affairs-21-320.jpg)







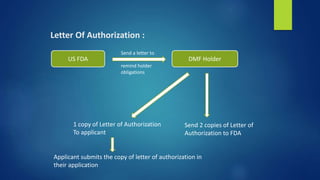
![ Transmittal Letter :
Original submissions and amendments ;
Identification of submission [ original / supportive to original
DMF
Type of DMF & Subject [ update, revised formula or revised
process ]
Name & address of each sponsor, applicant / holder & all
document numbers
Signature of holder
Type written name & title of signer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulatoryaffairs-181118095428/85/Regulatory-affairs-30-320.jpg)



![Applicable laws :
Food Drug and Cosmetic Act [ FD & C Act ]
Food Drug and Administration Safety Information Act [
FDASIA ]
The Generic Drug User Fee Act [ GDUFA ]
Prescription Drug User Fee Act [ PDUFA ]
Applicable Regulation :
314 New Drug Application [NDA] and
Abbreviated NDA [ANDA]
• 314.50 Content and Format of an application
• 314.70 Changes to an Approved Application
• 314.420 Drug Master Files](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulatoryaffairs-181118095428/85/Regulatory-affairs-35-320.jpg)



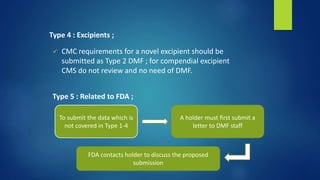
![ If there is no updation, then NDA, INDA, ANDA process will slow
down.
Any transfer of NDA / ANDA, the aim of transferring should be
mentioned as.,
• The name of the transfer
• Address of the transfer
• Name of responsible official for transferring
• Effective date of transferring
• Signature of the transferring official
• Title of the person
• Letter of acceptance [ Information given should be updated
after acceptance]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/regulatoryaffairs-181118095428/85/Regulatory-affairs-39-320.jpg)



