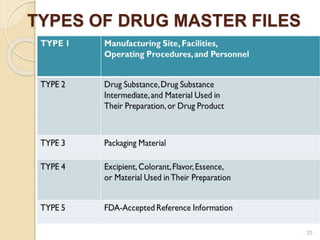
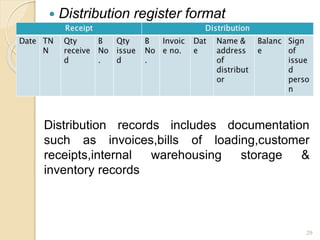
This document discusses documentation practices in the pharmaceutical industry. It emphasizes that quality cannot be ensured without good documentation, which involves systematic interaction between people, events, and documents. Documentation includes procedural documents, instructions, records, and various regulatory requirements. Records provide legally valid evidence and help ensure quality and consistency. The document then discusses specific documentation requirements like master formula records, drug master files, and distribution records. It provides examples of required information and formats for documentation.