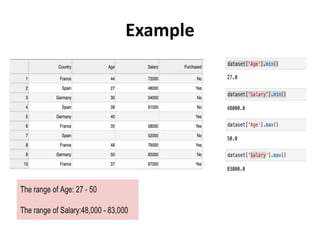
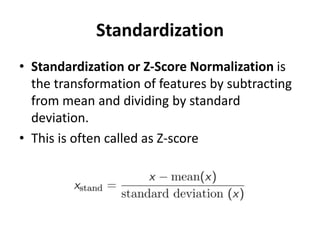
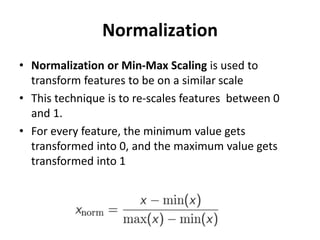
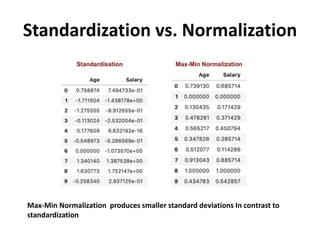
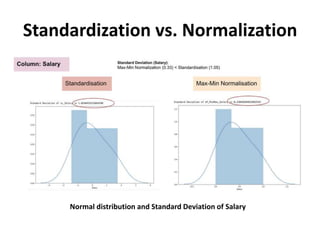
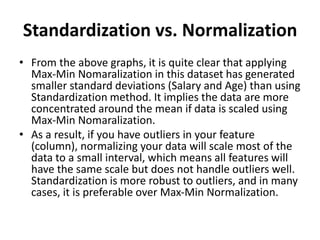
The document discusses data transformation techniques, specifically focusing on standardization and normalization, which are crucial for feature scaling in machine learning. It outlines the differences between these methods, their appropriate applications, and their impacts on datasets with varying scales, particularly emphasizing the importance of scaling in distance-based models. Standardization is noted for being more robust to outliers, while normalization is easier to apply but less effective in their presence.







![Standardization vs. Normalization
Normalization Standardization
Minimum and maximum value of features
are used for scaling
Mean and standard deviation is used for
scaling.
It is used when features are of different
scales.
It is used when we want to ensure zero
mean and unit standard deviation.
Scales values usually between [0, 1] It is not bounded to a certain range.
It is really affected by outliers. It is much less affected by outliers.
This transformation squishes the n-
dimensional data into an n-dimensional
unit hypercube.
It translates the data to the mean vector of
original data to the origin and squishes or
expands.
It is useful when we don’t know about the
distribution
It is useful when the feature distribution is
Normal or Gaussian.
It is a often called as Scaling Normalization It is a often called as Z-Score Normalization.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatransformationstandardizationnormalizationppm-240420122025-9e3e09d0/85/Data-Transformation-Standardization-Normalization-PPM-pptx-15-320.jpg)

