This document provides an overview of regression analysis, including:
- Regression analysis estimates relationships between dependent and independent variables and can be used for prediction and assessing variable influence.
- It mathematically determines which factors impact an outcome and which can be ignored.
- Simple and multiple linear regression fit linear equations to relate one or more explanatory variables to an outcome variable.
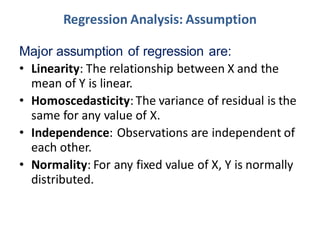
- Assumptions include linearity, homoscedasticity, independence, and normality.
- Regression analysis can infer causal relationships and is widely used for forecasting.