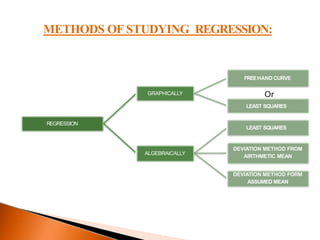
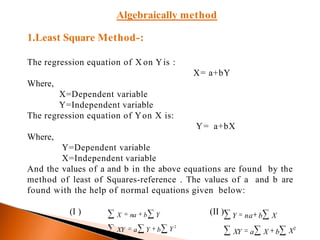
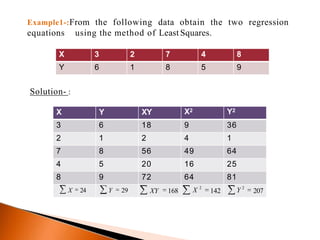
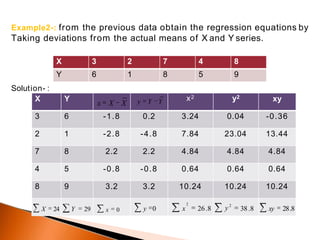
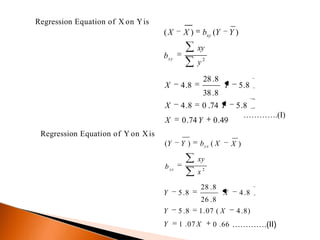
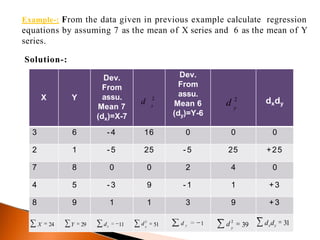
The document outlines the concept of regression analysis, which measures the relationship between variables and aids in prediction and forecasting. It explains the importance of regression in business and sociology, providing methods of calculation including least squares and deviation from the mean. Additionally, it presents example equations and gives methods for determining regression relationships using various techniques.