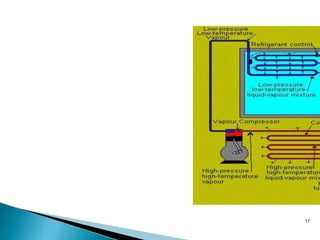
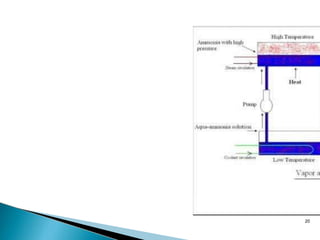
The document summarizes different refrigeration systems. It describes vapor compression refrigeration as the most important system for commercial and domestic use. It works by compressing a refrigerant like ammonia, carbon dioxide, or R-11 through different states - expansion, vaporization, compression, and condensation. Vapor absorption refrigeration uses ammonia absorbed and separated from water. Air refrigeration uses air as the refrigerant in the Bell Coleman cycle through a compressor, expander, and cooler.