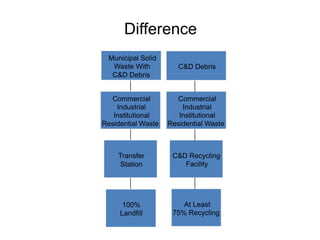
This document discusses the use and recycling of construction and demolition waste. It notes that demolition sites and restoration schemes generate large amounts of solid waste that is difficult and uneconomical to recycle. However, it is possible to reuse most building materials and components. The document outlines the types of materials that make up construction and demolition waste and provides examples of how materials like concrete, wood, metals, plastics and others can be recycled and reused in the construction industry. The benefits of recycling construction waste include reducing landfill waste, conserving resources and energy, and creating economic opportunities in recycling industries.