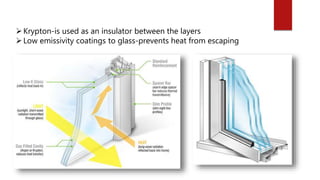
Sustainable building, or green building, aims to create structures that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout their life cycle, balancing home building with sustainable environmental goals. Key objectives include minimizing environmental impact, energy and water efficiency, protecting occupant health, and reducing waste. Sustainable materials are crucial, often derived from renewable sources or recycled waste, and while sustainable buildings offer various benefits such as energy efficiency and improved indoor air quality, they may face challenges like higher initial costs and the need for skilled labor.