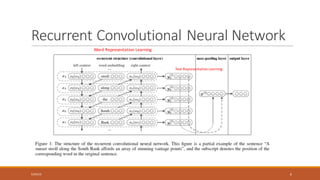
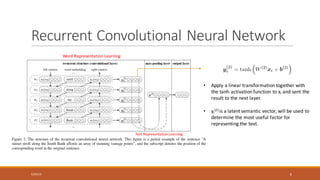
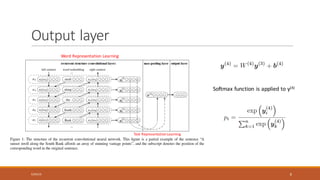
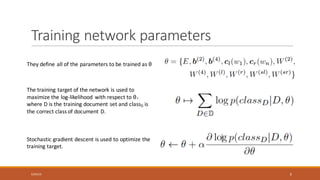
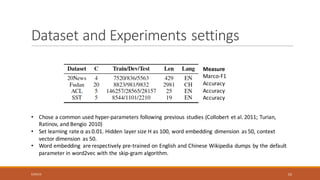
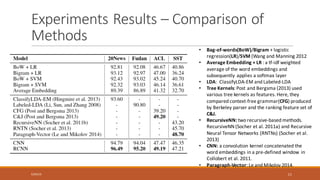
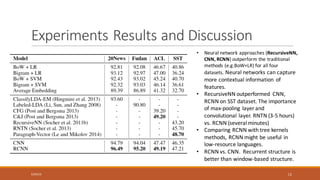
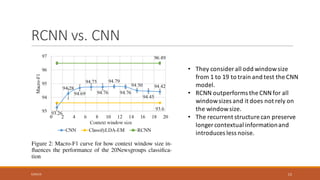
This document summarizes a research paper on Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks (RCNN) for text classification. RCNN was proposed to capture contextual information in text better than previous models like Recursive Neural Networks or Convolutional Neural Networks. It represents words based on their surrounding context, learns text representations using convolutions and max pooling, and classifies texts with a softmax output layer. Experiments on four text classification datasets found RCNN outperformed other models and was more efficient than Recursive Neural Tensor Networks, demonstrating its ability to learn important keywords for classification tasks.