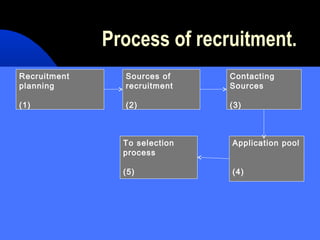
The document discusses recruitment, which is defined as the process of searching for prospective employees and encouraging them to apply for jobs. It covers the purpose and importance of recruitment, which includes determining staffing needs, increasing the candidate pool, and reducing turnover. Sources of recruitment include internal options like current employees or external options like advertisements. Methods of contacting candidates include direct recruitment like campus recruiting or indirect recruitment through ads. The recruitment process involves planning, contacting sources, building an applicant pool, and selecting candidates. The recruitment policy and process are then evaluated based on objectives, costs, and effectiveness.